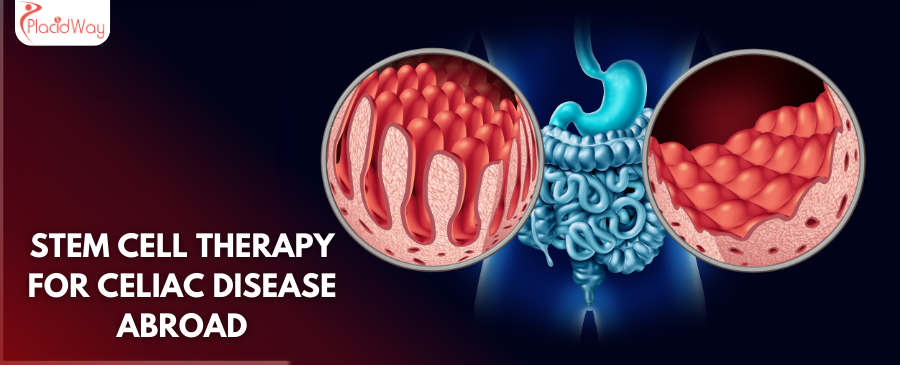
Finding Lasting Relief: Exploring Stem Cell Therapy for Celiac Disease
Living with Celiac Disease can be an relentless challenge. For many, a strict gluten-free diet brings significant relief, yet a persistent subset of patients continues to struggle with debilitating symptoms, even after diligently avoiding gluten. The constant pain, digestive distress, and fatigue can profoundly impact quality of life, leaving individuals searching for more effective, long-term solutions. If you find yourself among those still seeking answers, you're not alone. The search for advanced treatments often leads to exploring innovative medical frontiers, and one such area gaining attention is Stem Cell Therapy for Celiac Disease.
Celiac disease is more than just a food sensitivity; it's a serious autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. This damage hinders nutrient absorption and can cause a wide array of symptoms, from severe digestive issues like chronic diarrhea, bloating, and abdominal pain to non-digestive problems such as fatigue, anemia, skin rashes, and neurological symptoms. The ongoing inflammation and malabsorption can lead to significant health complications if left unmanaged.
While the gluten-free diet remains the cornerstone of conventional treatment, it doesn't always fully resolve symptoms for everyone. For those with refractory celiac disease or who experience continued gut damage despite dietary adherence, the prospect of repairing the intestinal lining and rebalancing the immune system is incredibly appealing. Stem cell therapy is an exciting, albeit evolving, field that holds promise for conditions where tissue regeneration and immune modulation are key. This page will delve into what stem cell therapy entails for celiac disease, who might benefit, what to expect, and why patients often consider traveling abroad for these advanced treatments.
Let’s explore the potential of this innovative approach and understand if it could be a viable path toward a better quality of life for you.
What are the common symptoms of Celiac Disease that impact daily life?
Celiac disease manifests differently in each individual, making diagnosis challenging. However, certain symptoms are highly prevalent and can significantly disrupt daily routines. These can be broadly categorized into digestive and non-digestive issues:
- Digestive Symptoms:
- Chronic Diarrhea or Constipation: Often described as loose, fatty stools or, paradoxically, persistent constipation.
- Abdominal Pain and Bloating: A feeling of fullness, gas, or cramping that can be severe.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Especially after consuming gluten.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained and often significant due to malabsorption.
- Non-Digestive Symptoms:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent tiredness, even after adequate rest, often linked to anemia or nutrient deficiencies.
- Anemia: Iron-deficiency anemia is common due to poor iron absorption, leading to paleness, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness.
- Skin Rashes (Dermatitis Herpetiformis): An intensely itchy, blistering rash, typically on elbows, knees, and buttocks. Many search for "celiac skin rash."
- Bone or Joint Pain: Aches in joints and bones, and increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Neurological Symptoms: Including headaches, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet (peripheral neuropathy), balance problems, and brain fog.
- Mouth Ulcers: Recurrent canker sores.
- Dental Enamel Defects: Especially in children.
- Depression and Anxiety: Mental health issues are frequently reported.
For those whose lives are continually impacted by these symptoms despite adherence to a gluten-free diet, the search for "new treatments for celiac disease" or "alternative celiac therapies" becomes crucial, leading them to explore advanced options like stem cell therapy.
What are the underlying causes and risk factors for developing Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease isn't caused by a single factor but is a complex interplay of genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and immune system dysfunction. Understanding these factors is key to recognizing the disease and exploring potential treatment avenues.
- Genetic Predisposition: The vast majority of people with celiac disease carry specific genes, primarily HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8. However, simply having these genes isn't enough; only about 2-3% of individuals with these genes develop celiac disease. This means other factors play a critical role.
- Gluten Exposure: Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, is the primary environmental trigger. When someone with celiac disease consumes gluten, their immune system mistakenly attacks the small intestine, specifically the villi (tiny, finger-like projections that absorb nutrients). This damage, known as villous atrophy, impairs nutrient absorption.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body's immune system, which is supposed to protect it from foreign invaders, turns against its own tissues. In celiac, the immune response to gluten is misguided and destructive.
- Risk Factors:
- Family History: Having a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, child) with celiac disease significantly increases your risk.
- Other Autoimmune Diseases: Individuals with other autoimmune conditions, such as Type 1 diabetes, autoimmune thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or Addison's disease, have a higher likelihood of developing celiac disease.
- Genetic Syndromes: Certain genetic disorders like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Williams syndrome are associated with a higher incidence of celiac disease.
- Microbiome Imbalance: Emerging research suggests that an imbalance in gut bacteria (dysbiosis) might also play a role in the development or severity of celiac disease.
For those struggling with its multifactorial nature and persistent symptoms, exploring "how to heal celiac damage" or "regenerative medicine for celiac" becomes a natural next step.
How does Stem Cell Therapy work for Celiac Disease and what types are available?
Stem cell therapy for celiac disease is an innovative approach that targets the core issues of the condition: intestinal damage and immune system dysregulation. While still an evolving field, the premise is to leverage the unique properties of stem cells to promote healing and restore balance.
How Stem Cells Might Help:
- Tissue Regeneration: Stem cells, particularly Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types. In celiac disease, they are believed to help repair the damaged intestinal villi, restoring the gut's ability to absorb nutrients. Imagine your small intestine as a lush garden; celiac disease creates barren patches. Stem cells are like expert gardeners, helping to re-plant and nourish the soil, allowing the villi to regrow and thrive.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: MSCs release powerful anti-inflammatory molecules that can dampen the chronic inflammation present in the celiac gut. This can reduce pain, discomfort, and further damage.
- Immunomodulation: Perhaps one of the most exciting aspects is their ability to modulate the immune system. MSCs can help 're-educate' the overactive immune cells that are mistakenly attacking the body's own tissues, potentially leading to a more tolerant and balanced immune response to gluten. This is key for an autoimmune condition like celiac.
Types of Stem Cells and Procedures:
The most commonly used stem cells for therapeutic applications in conditions like celiac disease are Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). These can be sourced from several areas:
- Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs): Extracted from a patient's own fat tissue through a mini-liposuction procedure. This is an autologous treatment, meaning it uses the patient's own cells, reducing rejection risk.
- Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells (BMSCs): Harvested from the patient's bone marrow. Also autologous.
- Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (UC-MSCs): Sourced from donated umbilical cord tissue after healthy births. These are allogeneic (from a donor) but are considered "immune privileged," meaning they typically do not provoke an immune response in the recipient. Many clinics abroad offer UC-MSC treatments due to their potency and ease of availability.
- Exosomes: While not stem cells themselves, exosomes are tiny vesicles released by stem cells that carry growth factors, proteins, and genetic material. They are being explored for their regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties.
The stem cells are typically administered intravenously (IV infusion) or sometimes locally via endoscopy, allowing them to travel to areas of inflammation and damage within the body. While research is ongoing, patients are seeking "celiac disease stem cell treatment options" as a beacon of hope for conditions that defy conventional management.
Who is an ideal candidate for Stem Cell Therapy for Celiac Disease?
Considering stem cell therapy for celiac disease is a significant decision, and not everyone is an ideal candidate. Clinics offering these advanced treatments have specific criteria to ensure safety and potential efficacy. Generally, candidates fall into categories where conventional treatments have proven insufficient:
- Refractory Celiac Disease (RCD): This is the primary group seeking innovative treatments. RCD is diagnosed when a patient continues to experience significant symptoms and villous atrophy despite adhering to a strict gluten-free diet for at least 12 months. RCD can be classified into two types (Type I and Type II), with Type II being more severe and less responsive to traditional therapies.
- Non-Responsive Celiac Disease (NRCD): Patients who don't fully recover on a gluten-free diet but don't meet the strict criteria for RCD. They may still experience persistent symptoms, malabsorption, and inflammation.
- Severe Symptoms: Individuals who suffer from debilitating symptoms that severely impact their quality of life, such as chronic pain, extreme fatigue, severe malabsorption leading to nutritional deficiencies, or neurological complications, may be considered.
- Good General Health: Despite having celiac disease, candidates should generally be in good overall health, free from other severe, uncontrolled medical conditions that could complicate the procedure or recovery. This includes a stable cardiovascular system and no active infections.
- Realistic Expectations: It's crucial for patients to understand that stem cell therapy for celiac is still an emerging field. While promising, it is not guaranteed to be a "cure" and outcomes can vary. A clear understanding of the experimental nature and potential benefits is essential.
- Thorough Diagnostic Workup: Candidates must have a confirmed diagnosis of celiac disease, often through biopsy, and a comprehensive medical history demonstrating the failure of standard treatments.
Eligibility is always determined after a detailed consultation with a qualified medical team, who will review your medical history, diagnostic tests, and current health status. They are looking for patients who truly need an alternative and have the best chance of benefiting from the therapy. This often prompts questions like "what are the criteria for celiac stem cell treatment?"
What is the typical recovery time and what can I expect after Stem Cell Therapy for Celiac?
The recovery experience after stem cell therapy for celiac disease is generally less intensive compared to many other medical procedures, but it's important to have realistic expectations regarding the timeline for potential improvements.
Immediate Post-Procedure:
- Minimal Downtime: Most stem cell treatments for celiac are performed on an outpatient basis. If you received an IV infusion, you might feel a bit tired or have mild flu-like symptoms for a day or two. If adipose-derived stem cells were used, there might be slight soreness, bruising, or swelling at the liposuction site.
- Observation: You'll likely be monitored for a short period after the infusion to ensure there are no immediate adverse reactions.
- Return to Normal Activities: Most patients can return to light normal activities within 24-48 hours. Strenuous exercise might be advised against for a few days to a week.
Long-Term Expectations and Timeline for Results:
- Gradual Improvement: Unlike a quick fix, stem cell therapy works by initiating a biological process of healing and regeneration. This takes time. Patients typically report noticing initial improvements within a few weeks to a few months after treatment.
- Continued Adherence to GF Diet: It's crucial to understand that stem cell therapy is not a license to abandon your gluten-free diet. You will still need to meticulously avoid gluten to prevent further immune reactions and damage, allowing the stem cells to do their work in a supportive environment.
- Follow-Up Care: Most clinics will recommend follow-up appointments, either in person or via telemedicine, to monitor your progress, re-evaluate symptoms, and potentially perform further diagnostic tests (like blood markers or repeat biopsies) to assess intestinal healing.
- Potential for Multiple Treatments: Depending on the severity of your condition and your response, some protocols may involve multiple stem cell infusions spaced over several months or years to achieve optimal results.
It's like planting a seed; you don't see the full bloom overnight. The stem cells need time to integrate, modulate the immune response, and facilitate tissue repair. Open communication with your medical team about your "celiac stem cell treatment expectations" is vital throughout this process.
What are the potential risks and side effects of Stem Cell Therapy for Celiac Disease?
As with any medical procedure, stem cell therapy carries potential risks and side effects, even though it is generally considered safe, particularly when using autologous (patient's own) cells or immune-privileged allogeneic cells like umbilical cord-derived MSCs. It's important to discuss these thoroughly with your medical provider.
- Minor and Temporary Side Effects:
- Injection Site Reactions: Pain, bruising, swelling, or tenderness at the site where cells were harvested (e.g., abdomen for fat) or infused (e.g., IV port).
- Mild Flu-like Symptoms: Fatigue, low-grade fever, headaches, or body aches can occur shortly after an IV infusion, usually resolving within 24-48 hours.
- Potential Risks (Rarer but More Serious):
- Infection: Any procedure involving injections or tissue harvesting carries a small risk of infection. This risk is minimized in sterile clinical environments.
- Allergic Reaction: Though rare, an allergic reaction to the stem cells themselves (especially allogeneic cells) or to components of the infusion solution can occur.
- Immune Response: While MSCs are generally considered immune-privileged, there's always a theoretical, albeit low, risk of an immune reaction, particularly with allogeneic cells, though protocols are designed to minimize this.
- Tumor Formation: A common concern with stem cell therapy is the potential for uncontrolled cell growth. However, with adult MSCs, the risk of tumor formation is considered extremely low, especially compared to embryonic stem cells. Reputable clinics use highly purified and characterized MSCs to mitigate this risk.
- Inefficacy: The therapy might not produce the desired results or improvements, especially given that it is an emerging treatment for celiac disease.
- Contamination: If cells are improperly handled or processed, there's a risk of bacterial or viral contamination. This highlights the importance of choosing a highly regulated and experienced clinic.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects of stem cell therapy for celiac disease are still being studied. This emphasizes the need for ongoing research and a careful, informed approach.
Choosing a reputable clinic with a strong track record, proper accreditation, and transparent communication about risks and benefits is paramount. This diligence helps address concerns about "celiac stem cell treatment safety."
How much does Stem Cell Therapy for Celiac Disease cost globally?
The cost of stem cell therapy for celiac disease is a major consideration for many patients, especially since it is often not covered by traditional health insurance due to its experimental or investigational status. The price can fluctuate wildly based on several factors, including the country, the clinic's reputation, the type of stem cells used, the number of cells administered, the number of treatment sessions, and included services.
Estimated Cost Comparison Table (USD, per treatment cycle)
| Country/Region | Estimated Cost Range (USD) | Notes on Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| United States | $15,000 - $50,000+ | Highest costs due to regulatory environment, research, and overhead. Often part of clinical trials. |
| Mexico | $8,000 - $25,000 | Popular medical tourism destination; competitive pricing, access to advanced therapies. |
| Panama | $10,000 - $30,000 | Known for reputable clinics and favorable regulatory environment for stem cell research. |
| Germany | $12,000 - $35,000 | High standards of medical care and well-regulated clinics. |
| India / Thailand | $7,000 - $20,000 | Emerging medical tourism hubs offering lower costs with increasing quality of care. |
Factors Influencing Cost:
- Type of Stem Cells: Autologous treatments (using your own cells) often involve a harvesting procedure, which can add to the cost. Allogeneic cells (from a donor, like umbilical cord) may have different pricing structures.
- Number of Cells: Higher cell counts or more concentrated doses can increase the price.
- Treatment Protocol: Some conditions may require a single infusion, while others benefit from multiple sessions, increasing the overall cost.
- Included Services: The total price might include initial consultations, diagnostic tests, post-treatment follow-ups, medication, and sometimes even travel coordination or accommodation.
- Clinic Reputation and Expertise: Highly specialized clinics with renowned doctors and advanced facilities often command higher prices.
It's crucial to obtain a detailed, itemized quote from any clinic you consider to understand exactly what's included in the "celiac stem cell treatment price."
Why should I consider traveling abroad for Stem Cell Therapy for Celiac Disease?
For individuals seeking advanced treatments for celiac disease, especially those with refractory or non-responsive forms, medical tourism has become a compelling option. The decision to travel internationally for healthcare is often driven by several key factors:
- Access to Innovative Treatments: Stem cell therapy for celiac disease is still considered experimental in many countries. Abroad, particularly in countries with more progressive regulatory environments, certain clinics may offer these cutting-edge therapies before they become widely available or approved elsewhere. This provides an opportunity for patients to access "new treatments for celiac disease."
- Competitive Pricing: As seen in the cost comparison, the financial burden of advanced therapies can be significantly lower in certain medical tourism destinations compared to Western countries, without necessarily compromising quality. This makes treatment more accessible for those without insurance coverage.
- Specialized Expertise and Focus: Many international clinics specialize exclusively in regenerative medicine and stem cell therapies, attracting highly skilled specialists who have extensive experience in these specific areas. They often have dedicated protocols and infrastructure tailored for such treatments.
- Reduced Wait Times: In some domestic healthcare systems, long wait times for consultations, diagnostic tests, and treatments can be a significant barrier. Medical tourism often provides quicker access to appointments and procedures, allowing patients to begin their treatment sooner.
- Comprehensive Care Packages: Many clinics abroad offer all-inclusive packages that cover not just the medical procedure but also accommodation, airport transfers, translation services, and even post-treatment recovery support, simplifying the entire process for international patients.
- Privacy and Discretion: Some patients prefer the anonymity and privacy that comes with receiving treatment in another country, away from their local community or workplace.
- Holistic and Personalized Approach: Many international stem cell clinics pride themselves on a more patient-centric and holistic approach, often integrating complementary therapies and offering highly personalized treatment plans.
Ultimately, the decision to seek "celiac disease treatment abroad" is personal, but these advantages highlight why a growing number of patients are looking beyond their borders for hope and healing.
Which countries are recognized for offering advanced Stem Cell Therapy for Celiac Disease?
When considering medical tourism for stem cell therapy for celiac disease, certain countries have established reputations for their advanced medical facilities, favorable regulatory environments for regenerative medicine, and competitive pricing. Here are some of the frequently chosen destinations:
- Mexico:
- Why: Close proximity to the U.S., significantly lower costs, and a growing number of clinics specializing in stem cell therapies. Cities like Tijuana, Cancun, and Guadalajara have become hubs for medical tourism.
- Focus: Many clinics offer adipose-derived or umbilical cord-derived MSCs, often with comprehensive patient support.
- Panama:
- Why: Panama has a progressive regulatory framework for stem cell research and treatment, attracting top scientists and clinicians. It's often cited for its high standards and ethical approach.
- Focus: Known for its dedicated stem cell research centers and clinics utilizing various MSC sources.
- Germany:
- Why: Renowned for its stringent medical standards, advanced research, and highly qualified physicians. German clinics offer a blend of cutting-edge treatments and rigorous quality control.
- Focus: Often concentrates on autologous treatments, with a strong emphasis on evidence-based practices.
- Cayman Islands:
- Why: A luxurious destination with state-of-the-art medical facilities and a favorable regulatory environment for regenerative medicine. Offers a high-end medical tourism experience.
- Focus: Specialized clinics offering advanced stem cell therapies, often with a focus on patient comfort and comprehensive care.
- India & Thailand:
- Why: These Asian countries offer highly competitive pricing, English-speaking staff, and modern medical infrastructure. They have rapidly developed into major medical tourism destinations.
- Focus: A wide range of stem cell therapies are available, with some clinics focusing on specific conditions like autoimmune disorders.
Choosing the "top stem cell clinics for celiac" requires thorough research into their accreditation, doctor qualifications, specific protocols, and patient testimonials.
How to ensure safety and quality when seeking Celiac Stem Cell Therapy abroad?
Ensuring safety and quality when undergoing any medical procedure abroad, especially an emerging one like stem cell therapy for celiac disease, is paramount. Diligence and informed decision-making are your best allies. Here’s a checklist to guide your search for "safe stem cell therapy abroad":
- Accreditation and Licensing:
- International Accreditation: Look for clinics accredited by recognized international bodies like Joint Commission International (JCI), which signifies adherence to global healthcare standards.
- Local Licensing: Ensure the clinic is fully licensed and regulated by the local health authorities in its country.
- Doctor Credentials and Experience:
- Specialization: Verify that the doctors are board-certified in relevant fields (e.g., gastroenterology, regenerative medicine) and have specific experience in stem cell therapy for autoimmune or gastrointestinal conditions.
- Research and Publications: Clinicians involved in research or publishing in peer-reviewed journals often indicate a commitment to evidence-based practice.
- Transparency in Treatment Protocols:
- Specifics of Therapy: Demand clear information about the type of stem cells used (e.g., adipose, umbilical cord), their source, processing methods, and the number of cells administered.
- Patient-Specific Plan: Ensure they offer a personalized treatment plan tailored to your condition, rather than a generic protocol.
- Clear Communication: The clinic should be transparent about potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes, setting realistic expectations. Be wary of clinics that promise a "cure."
- Facility Standards:
- Sterility and Equipment: Inquire about their lab facilities, sterilization procedures, and the technology used for cell processing and administration. A clean, modern facility is a good indicator.
- Emergency Preparedness: Understand their protocols for handling potential complications or medical emergencies.
- Comprehensive Patient Support:
- Pre-treatment Evaluation: A thorough medical review before treatment is essential to determine eligibility and customize the therapy.
- Post-treatment Follow-up: Inquire about their plan for post-procedure monitoring, follow-up consultations, and ongoing support, which might include remote consultations.
- Language and Logistics: Ensure there are clear communication channels (e.g., English-speaking staff, translators) and support for travel logistics.
- Patient Testimonials and Reviews:
- While individual results vary, reading reviews and testimonials on independent platforms can offer insights into other patients' experiences with the clinic's care and outcomes.
Working with a reputable medical tourism facilitator like PlacidWay can significantly aid in vetting clinics and ensuring a safe, high-quality experience for "celiac disease treatment abroad."
What are patient success stories from abroad for Celiac Stem Cell Therapy?
The journey for effective Celiac Disease treatment is deeply personal, and while scientific research progresses, the real-world impact is often best understood through patient experiences. While stem cell therapy for celiac is still emerging, anecdotally, many individuals who have traveled abroad for these treatments report positive outcomes, finding renewed hope where conventional methods fell short.
Imagine Sarah, a 45-year-old from Canada, who had been diagnosed with refractory celiac disease for years. Despite a meticulous gluten-free diet, she suffered from chronic debilitating fatigue, anemia, and severe abdominal pain, making it impossible to work or enjoy time with her family. After extensive research, she decided to pursue stem cell therapy at a specialized clinic in Panama. Within three months, Sarah reported a significant reduction in her fatigue, improved energy levels, and a noticeable decrease in her abdominal discomfort. Her latest blood tests even showed improved iron levels, a welcome change after years of anemia. While she still maintained her gluten-free diet, the quality of her life had dramatically improved, allowing her to regain a sense of normalcy.
Or consider David, a 58-year-old from the UK, who developed dermatitis herpetiformis alongside severe digestive issues, even after a strict adherence to a gluten-free diet. The incessant itching and skin lesions were unbearable. After receiving umbilical cord-derived MSCs in Mexico, David experienced a gradual clearing of his skin rash and a substantial reduction in his digestive inflammation. He described feeling a "quieting" of his immune system, and while not completely symptom-free, the severity of his condition was profoundly lessened, allowing him to enjoy activities he had given up years ago.
These stories, echoed in numerous patient testimonials online and through medical tourism platforms, highlight the potential for stem cell therapy to offer relief and significantly improve the quality of life for those struggling with persistent celiac symptoms. It's important to remember that these are individual experiences and outcomes can vary. However, they serve as powerful examples of why patients continue to explore "stem cell therapy for celiac disease patient reviews" and "medical tourism for celiac success stories" as they navigate their own paths to healing.
Take the Next Step with PlacidWay
Ready to explore treatment options abroad? Discover top clinics, compare prices, and get a free quote tailored to your needs with PlacidWay.
Stem Cell Therapy Abroad








Share this listing