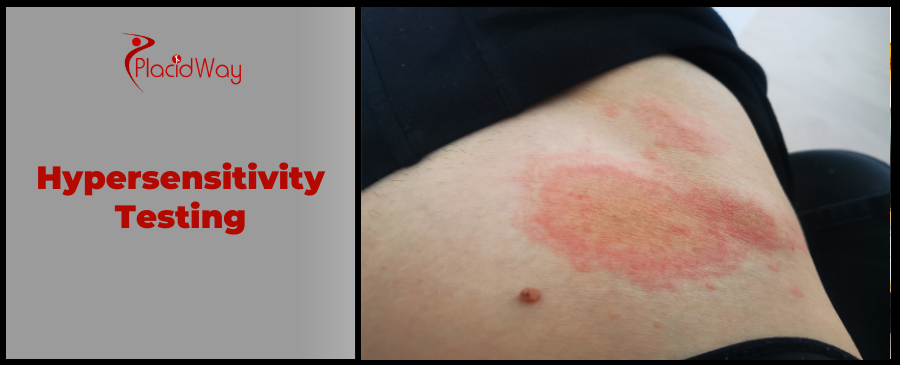
Uncover Your Triggers: Comprehensive Hypersensitivity Testing for Lasting Relief
Living with unexplained rashes, constant sneezing, digestive upsets, or even frightening reactions to certain foods or medications can be frustrating and debilitating. These symptoms often point to hypersensitivity reactions, where your immune system overreacts to a typically harmless substance. But pinpointing the exact trigger can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. This is where Hypersensitivity Testing becomes your crucial ally.
Imagine finally understanding why certain foods make you feel ill, or why you break out in hives after using a new product. Hypersensitivity testing provides the answers, offering clarity and a path towards managing your condition more effectively. For many, seeking this specialized diagnostic care abroad through medical tourism offers access to advanced facilities, expert allergists, and often more affordable options without compromising on quality.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about hypersensitivity testing – from understanding your symptoms and potential causes to exploring various testing methods, costs, and why medical tourism might be the ideal solution for you. Let's embark on this journey to better health and lasting relief.
What symptoms suggest you need hypersensitivity testing?
Recognizing the signs your body sends is the first step towards seeking help. Hypersensitivity reactions can manifest in a myriad of ways, ranging from mild irritation to severe, life-threatening conditions. Here are common symptoms that might signal the need for hypersensitivity testing:
- Skin Issues: Chronic hives (urticaria), eczema (atopic dermatitis), persistent itching, contact dermatitis (rashes from touching certain substances).
- Respiratory Problems: Persistent sneezing, runny nose, nasal congestion, itchy eyes, asthma attacks, shortness of breath, recurrent sinus infections.
- Digestive Complaints: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, particularly after consuming certain foods.
- Severe Reactions: Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema), difficulty swallowing, dizziness, sudden drop in blood pressure, or anaphylaxis – a severe, whole-body allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention.
- Drug Reactions: Rashes, itching, swelling, or breathing difficulties after taking certain medications.
If you experience any of these symptoms regularly, especially if they worsen or interfere with your daily life, consulting a healthcare professional for potential hypersensitivity testing is highly recommended. These tests can identify what's causing your discomfort and help you avoid future reactions.
What causes hypersensitivity reactions in the body?
At its core, a hypersensitivity reaction is an overzealous response by your immune system. Instead of identifying a substance as benign, it mistakenly perceives it as a threat, mounting an attack that results in allergic symptoms. The exact causes are complex and often multifaceted:
- Genetic Predisposition: Allergies often run in families. If one or both of your parents have allergies or asthma, you're at a higher risk of developing them.
- Environmental Exposure: Repeated exposure to allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, or certain chemicals can sensitize your immune system over time.
- Food Allergens: Common culprits include peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish. These can trigger immediate and sometimes severe reactions.
- Drug Allergies: Certain medications, such as antibiotics (e.g., penicillin), NSAIDs (e.g., aspirin), and some chemotherapy drugs, can cause allergic responses.
- Insect Stings: Venom from bees, wasps, hornets, and fire ants can trigger severe allergic reactions in sensitized individuals.
- Contact Allergens: Substances like nickel, latex, certain fragrances, cosmetics, and dyes can cause localized skin reactions upon contact.
Understanding the potential causes helps in narrowing down the possibilities and guiding the appropriate testing. It's not always about avoiding the trigger entirely, but about identifying it to manage exposure and prepare for potential reactions.
What are the different types of hypersensitivity testing available?
There are several diagnostic tools available, each tailored to detect different types of hypersensitivity reactions. An allergist will determine the most appropriate test based on your symptoms and medical history:
- Skin Prick Test (SPT):
- How it works: Small amounts of potential allergens are pricked onto the skin (usually the forearm or back).
- What it detects: Immediate allergic reactions (Type I hypersensitivity) to airborne allergens (pollen, dust mites), pet dander, insect stings, and some foods.
- Results: A raised, red bump (wheal) within 15-20 minutes indicates a positive reaction.
- Patch Test:
- How it works: Allergens are applied to patches, which are then placed on the skin (usually the back) for 48-72 hours.
- What it detects: Delayed allergic reactions (Type IV hypersensitivity), primarily for contact dermatitis caused by substances like metals, chemicals, or cosmetics.
- Results: Redness, swelling, or blistering under the patch indicates a positive reaction after the patches are removed and read.
- Blood Tests (Specific IgE, IgG, etc.):
- How it works: A blood sample is taken and sent to a lab to measure specific antibodies.
- Specific IgE (RAST, ImmunoCAP): Measures the level of immunoglobulin E antibodies to specific allergens in the blood. Often used when skin tests are not possible or safe. Detects Type I hypersensitivity.
- Specific IgG/IgA: While controversial and not universally accepted for true allergies, some clinics offer tests for IgG or IgA antibodies, often marketed for "food intolerances" or sensitivities. Patients seeking comprehensive gut health evaluations often inquire about these tests.
- Results: Higher levels of specific antibodies suggest sensitivity to that allergen.
- Oral Food/Drug Challenge:
- How it works: Under strict medical supervision, increasing amounts of a suspected food or drug are given to the patient, observing for reactions.
- What it detects: Considered the "gold standard" for diagnosing food and drug allergies, especially when other tests are inconclusive.
- Results: Any allergic symptoms during the challenge confirm the allergy.
Who is eligible for hypersensitivity testing and when should it be considered?
Deciding when and if to pursue hypersensitivity testing is an important discussion to have with a healthcare provider. Generally, you should consider testing if you:
- Experience Persistent or Recurrent Symptoms: If you constantly have unexplained rashes, sneezing, wheezing, or digestive issues that don't resolve.
- Have Had Severe Reactions: Especially if you've experienced anaphylaxis, severe swelling, or breathing difficulties after exposure to a suspected allergen.
- Suspect Food Allergies or Intolerances: If certain foods consistently cause digestive upset, skin reactions, or other allergic symptoms.
- Need to Identify Drug Allergies: Before starting new medications or if you've reacted poorly to drugs in the past.
- Have Occupational Allergies: If your work environment seems to trigger allergic symptoms.
- Are Considering Allergy Treatments: Such as immunotherapy, which requires precise identification of your allergens.
- Have a Family History of Allergies: Even without immediate symptoms, understanding your predispositions can be valuable.
Eligibility is typically broad, but certain conditions might temporarily delay testing, such as recent severe allergic reactions, ongoing medication use (e.g., antihistamines that can interfere with skin tests), or active skin conditions. A thorough medical evaluation will determine if and when you are ready for testing.
What should you expect during recovery after hypersensitivity testing?
The "recovery" period for hypersensitivity testing is usually minimal, allowing most individuals to return to their daily routines immediately. What you experience largely depends on the type of test performed:
- Skin Prick Test:
- You might experience small, itchy, red bumps (like mosquito bites) at positive test sites. These usually subside within a few hours.
- Over-the-counter antihistamines (after the test, if approved by your doctor) or a cool compress can help alleviate itching.
- There's no downtime, and you can resume normal activities immediately.
- Patch Test:
- After the patches are removed (typically after 48 hours) and the results are read (often at 72 or 96 hours), any positive reactions will appear as localized redness, itching, or swelling.
- These reactions can persist for several days. Your doctor might recommend topical corticosteroids to soothe the skin.
- Avoid excessive sweating or showering vigorously during the patch application period.
- Blood Test:
- The only "recovery" involves a small bruise or tenderness at the site where blood was drawn, which resolves quickly.
- You can resume all activities immediately.
- Oral Food/Drug Challenge:
- This procedure requires the most significant post-test observation. You will remain in the clinic under medical supervision for several hours after the challenge to monitor for any delayed reactions.
- If a reaction occurs, you will receive immediate treatment.
- Once stable and discharged, you may feel tired but can usually resume light activities.
In all cases, your medical team will provide specific post-test instructions and explain what to watch for. It's rare to have prolonged discomfort beyond localized irritation, but always communicate any concerns.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with hypersensitivity testing?
While hypersensitivity testing is generally very safe, especially when conducted by experienced professionals, it's important to be aware of potential risks and side effects:
- Mild Localized Reactions: The most common side effect for skin tests is localized itching, redness, and swelling at the test site. This is usually transient and manageable with over-the-counter remedies.
- Fainting or Dizziness: Some individuals may feel lightheaded or faint during blood draws or due to anxiety.
- False Positives/Negatives: No test is 100% accurate. Medications (like antihistamines) can interfere with skin tests, leading to false negatives. Cross-reactivity between allergens can sometimes lead to false positives.
- Allergic Reaction (Rare but Serious):
- Skin Prick/Patch Tests: Extremely rarely, a skin test can trigger a systemic allergic reaction (like hives all over the body or even anaphylaxis). This is why tests are performed in a medical setting where emergency equipment and medication are readily available.
- Oral Food/Drug Challenges: Since these tests intentionally expose you to the suspected allergen, there's a higher chance of triggering a reaction, which is why they are performed under strict medical supervision with emergency protocols in place.
Always disclose all medications you are taking, your full medical history, and any previous severe reactions to your allergist. This allows them to assess your risk profile and take necessary precautions to ensure your safety during testing.
How much does hypersensitivity testing cost globally?
The cost of hypersensitivity testing can be a significant factor for many patients, especially if insurance coverage is limited or non-existent. Prices vary widely depending on:
- Country and Region: Healthcare costs differ drastically across nations.
- Type of Test: A simple skin prick test is generally less expensive than a comprehensive blood panel or an oral challenge.
- Number of Allergens Tested: The more substances tested, the higher the cost.
- Clinic and Specialist Fees: Highly specialized clinics or renowned allergists may charge more.
- Inclusions: Some packages include initial consultation, follow-up, and interpretation, while others charge separately.
Here's a general cost comparison (estimates in USD):
| Country | Skin Prick Test (e.g., 20 allergens) | Specific IgE Blood Test (per allergen) | Comprehensive Allergy Panel (Blood) |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA / Canada | $300 - $800 | $50 - $150 | $800 - $3000+ |
| UK / Western Europe | $250 - $700 | $40 - $120 | $700 - $2500+ |
| Mexico / Turkey / Thailand / India | $100 - $400 | $20 - $80 | $300 - $1200+ |
These figures are estimates and can fluctuate. The cost savings in medical tourism destinations like Mexico, Turkey, Thailand, or India can be substantial, often 50% to 70% less than in North America or Western Europe, even when factoring in travel expenses.
Why should you consider traveling abroad for hypersensitivity testing?
For many patients, especially those facing high costs, long wait times, or limited access to specific tests in their home country, medical tourism presents a compelling solution for hypersensitivity testing:
- Cost Savings: As seen in the table above, the most significant driver is often the substantial reduction in cost for high-quality care, making advanced diagnostics accessible to more people.
- Access to Specialized Expertise: Many international clinics boast world-class allergists and immunologists who specialize in complex hypersensitivity cases and employ the latest diagnostic protocols.
- Advanced Testing Options: Some countries and clinics offer a broader range of tests, including more detailed food sensitivity panels (beyond standard IgE), or are early adopters of new diagnostic technologies.
- Reduced Wait Times: In countries with universal healthcare systems or high demand, wait times for specialist appointments and testing can be months. Abroad, you can often schedule your tests within weeks or even days.
- Privacy and Anonymity: For some, the anonymity offered by receiving treatment away from home is appealing.
- Combination with Travel: Patients can combine their medical trip with a vacation, turning a necessary procedure into a more positive experience.
Considering the comprehensive benefits, traveling abroad for hypersensitivity testing is becoming an increasingly popular choice for savvy medical tourists.
Which countries are best known for affordable and quality hypersensitivity testing?
Several countries have emerged as leading destinations for medical tourism, particularly for diagnostic services like hypersensitivity testing, due to their balance of quality, affordability, and accessibility:
- Turkey: Renowned for its modern, JCI-accredited hospitals, state-of-the-art technology, and highly skilled specialists. Istanbul and Ankara offer excellent allergy clinics at competitive prices.
- Mexico: A top choice for North American patients due to proximity. Cities like Tijuana, Cancun, and Guadalajara have excellent private hospitals and clinics offering a full range of allergy tests.
- Thailand: Known for its exceptional hospitality and world-class medical facilities, particularly in Bangkok and Phuket. Thai clinics offer comprehensive allergy testing with competitive pricing.
- India: A powerhouse in medical tourism, offering highly advanced medical care, including allergy diagnostics, at a fraction of Western costs. Chennai, Bangalore, and Delhi are key medical hubs.
- Poland/Hungary (Eastern Europe): These countries offer high-quality medical services at lower costs than their Western European counterparts. They are popular for European patients seeking value.
When choosing a destination, it's crucial to research specific clinics, look for international accreditations (like JCI), and read patient reviews to ensure both quality of care and patient safety.
What should patients expect when traveling for hypersensitivity testing abroad?
Traveling for medical procedures requires careful planning. Here’s a general overview of what to expect:
- Initial Research & Consultation:
- Medical Tourism Facilitator: Companies like PlacidWay specialize in connecting you with reputable clinics abroad, helping with quotes, appointments, and logistics.
- Share Medical History: You'll need to send your medical records, current symptoms, and any previous test results to the chosen clinic for an initial assessment.
- Virtual Consultation: Many clinics offer video consultations with their allergists to discuss your case and recommend appropriate tests.
- Planning Your Trip:
- Travel & Accommodation: Book flights and arrange lodging. Many clinics or facilitators offer assistance with this, sometimes even providing airport transfers.
- Visa Requirements: Check if you need a visa for your chosen destination.
- Medication Review: Discuss with your foreign doctor which medications (especially antihistamines) you need to stop before testing, and for how long.
- During Your Stay:
- Arrival & Local Support: You may be met at the airport. A local coordinator might assist with appointments and translation.
- Pre-Test Consultation: A detailed in-person consultation with the allergist, including a physical exam, before any testing begins.
- Testing Procedure: The actual hypersensitivity tests will be performed as scheduled. This may take a few hours or multiple visits over a few days for tests like patch tests.
- Results & Follow-up: You'll typically receive your results and a detailed explanation, including a management plan, before you return home.
- Post-Trip Care:
- Communication: Ensure you have a clear plan for post-test communication with your foreign medical team for any questions or concerns.
- Share with Home Doctor: It's advisable to share your results and treatment plan with your local doctor for continuity of care.
Preparation and clear communication are paramount to a successful medical tourism experience.
Take the Next Step with PlacidWay
Ready to explore treatment options abroad? Discover top clinics, compare prices, and get a free quote tailored to your needs with PlacidWay.
General Medicine








Share this listing