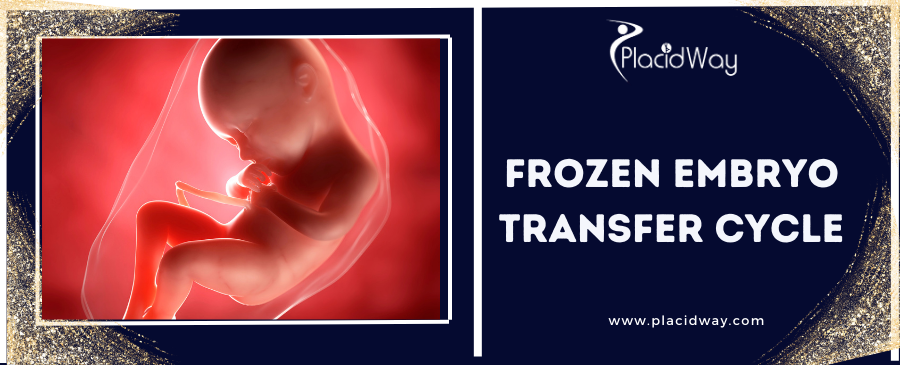
Realizing Your Dream: Understanding the Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) Cycle
Navigating the path to parenthood can be a complex and emotional journey for many. When faced with fertility challenges, In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) often emerges as a beacon of hope. Within the world of IVF, the Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) cycle stands out as a crucial and increasingly popular step for couples and individuals aiming to conceive.
A Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) cycle is a sophisticated procedure where embryos, which were previously created and cryopreserved (frozen) during an earlier IVF cycle, are thawed and then transferred into a woman's uterus. This method has revolutionized fertility treatment, offering significant advantages such as improved success rates, reduced risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), and the flexibility to plan future pregnancies.
For those considering "fertility treatment abroad" or exploring "affordable IVF options," understanding the FET cycle is paramount. It's often chosen after a successful fresh IVF cycle yields surplus embryos, or when medical reasons necessitate delaying the embryo transfer. Whether you're researching "FET success rates," "cost of embryo transfer," or "what to expect during FET," this guide aims to provide comprehensive, empathetic, and clear answers to help you make informed decisions on your journey to building a family.
What Are the Conditions or Symptoms Leading to a Frozen Embryo Transfer?
The primary "symptom" leading to a Frozen Embryo Transfer is the inability to conceive naturally, often diagnosed as infertility after a year of unprotected intercourse (or six months if over 35). More specifically, FET becomes relevant in several scenarios:
- Previous IVF Cycle with Surplus Embryos: This is the most common reason. If a fresh IVF cycle produces multiple high-quality embryos, some are transferred immediately (fresh transfer), and the remaining healthy embryos are frozen for future use. If the fresh transfer doesn't result in pregnancy, or if the couple wishes for another child later, these frozen embryos can be used.
- Failed Fresh Embryo Transfer: For many, a FET offers a second, third, or even fourth chance at pregnancy if previous fresh or frozen transfers were unsuccessful.
- Risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): In some fresh IVF cycles, a woman's ovaries overreact to fertility medications. Transferring embryos in this state can exacerbate OHSS. Freezing all embryos and performing an FET later, once the ovaries have recovered, significantly reduces this risk.
- Uterine Lining Issues: Sometimes, the uterine lining isn't optimally prepared during a fresh cycle. Freezing allows time to improve the lining before transfer.
- Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT): If embryos undergo genetic screening (PGT-A for aneuploidy or PGT-M for specific genetic conditions), they are typically frozen while awaiting test results, and then a healthy embryo is transferred in a subsequent FET cycle.
- Medical Reasons: Other medical conditions requiring a delay, such as severe illness, or treatments that could harm a developing embryo, might necessitate freezing embryos for a later transfer.
- Family Planning: Couples may opt for FET to space out pregnancies, using embryos from the same IVF cycle for subsequent children.
What Are the Common Causes and Risk Factors for Needing IVF & FET?
The journey to IVF and subsequently FET often begins with an underlying infertility diagnosis. Understanding the "causes of infertility" is crucial for appropriate treatment. These causes can be attributed to female factors, male factors, or a combination of both, sometimes remaining "unexplained infertility."
Common Female Factors:
- Ovulatory Disorders: Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), premature ovarian failure, or hypothalamic dysfunction can disrupt ovulation.
- Blocked or Damaged Fallopian Tubes: Often caused by pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, or previous surgeries, preventing egg and sperm from meeting.
- Endometriosis: A condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, affecting fertility.
- Uterine Fibroids or Polyps: Non-cancerous growths that can interfere with embryo implantation.
- Reduced Ovarian Reserve: A decline in the quantity and quality of eggs, most commonly due to advanced maternal age (over 35).
Common Male Factors:
- Abnormal Sperm Production or Function: Low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormally shaped sperm.
- Erectile Dysfunction or Ejaculation Problems: Issues preventing sperm delivery.
- Genetic Conditions: Certain genetic disorders can impact sperm quality.
- Testicular Trauma or Disease: Injury or illness affecting sperm production.
Other Risk Factors:
- Advanced Maternal Age: The most significant factor, as egg quality and quantity decline with age.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and extreme weight can impact fertility for both partners.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic illnesses, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
- Unexplained Infertility: When no clear cause can be identified despite extensive testing.
When these factors prevent natural conception or make it highly unlikely, IVF becomes a viable option, often leading to the cryopreservation of embryos and subsequent FET cycles.
What Are the Different Types of Frozen Embryo Transfer Cycles?
There are generally two main "types of FET" cycles, each tailored to the individual patient's hormonal profile and needs. The goal of both is to create an optimal uterine environment for embryo implantation.
1. Programmed (Hormone Replacement Therapy - HRT) Cycle:
This is the most common type of FET cycle, especially for women with irregular menstrual cycles or those who may not ovulate reliably. It involves:
- Estrogen Priming: The patient takes estrogen (pills, patches, or injections) for about two to three weeks to thicken the uterine lining (endometrium).
- Progesterone Administration: Once the lining reaches an optimal thickness, progesterone (vaginal suppositories, gel, or injections) is added. This hormone prepares the lining for implantation and supports early pregnancy. The embryo transfer is timed precisely after a few days of progesterone.
- Advantages: Predictable scheduling, tight control over the uterine environment, and can be used for women who don't ovulate or have gone through menopause.
2. Natural Cycle FET:
This approach harnesses the woman's natural menstrual cycle, relying on her body's own hormonal fluctuations. It's usually suitable for women with regular menstrual cycles and predictable ovulation.
- Monitoring Ovulation: The cycle involves monitoring the woman's natural hormonal changes, usually with blood tests and ultrasounds, to detect the growth of a dominant follicle and pinpoint ovulation.
- Progesterone Production: After natural ovulation, the body naturally produces progesterone. The embryo transfer is timed based on the expected day of ovulation.
- Advantages: Less medication, potentially fewer side effects, and some studies suggest it may be more physiologically similar to natural conception.
- Disadvantages: Requires more frequent monitoring and less predictable scheduling.
3. Modified Natural Cycle FET:
A hybrid approach where the natural cycle is monitored, but a "trigger shot" (e.g., hCG) is used to induce ovulation at a precise time. Progesterone support might also be added after ovulation, but the primary estrogen surge is still natural.
The choice between these cycles is made in consultation with your fertility specialist, considering your medical history, ovarian function, and previous IVF outcomes.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for a Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)?
Understanding "who can get FET" is important for anyone considering this fertility treatment. An ideal candidate for a Frozen Embryo Transfer typically shares several key characteristics:
- Existence of Frozen Embryos: The most fundamental requirement is having viable, high-quality embryos that were previously cryopreserved from an earlier IVF cycle. This could be due to surplus embryos, a 'freeze-all' approach, or PGT.
- Good Uterine Health: The uterus must be healthy and receptive to implantation. This means no significant uterine abnormalities (like large fibroids or polyps) that could interfere with pregnancy. A thin or irregular uterine lining could be a contraindication, though often treatable.
- Overall Good Health: Candidates should be in good general health, free from active infections or serious medical conditions that would make pregnancy risky. Your doctor will conduct a thorough medical evaluation.
- Stable Hormonal Environment: Whether through natural cycles or hormone replacement, the body must be able to support a stable hormonal environment conducive to embryo implantation and early pregnancy.
- Desire to Avoid OHSS: If a patient is at high risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome during a fresh cycle, a 'freeze-all' strategy followed by a FET in a subsequent cycle makes them an ideal candidate.
- Need for Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT): Patients whose embryos undergo genetic screening are ideal candidates for FET, as the embryos are frozen while awaiting test results.
- Family Planning Considerations: Couples who successfully conceived with a fresh transfer and wish to have another child later often use their remaining frozen embryos, becoming ideal FET candidates for subsequent pregnancies.
- Emotional Readiness: While not a medical criterion, being emotionally prepared for the process, including the two-week wait and potential outcomes, is vital.
It's always essential to consult with a fertility specialist to determine if you are an ideal candidate for FET based on your unique medical history and circumstances.
What Can I Expect During the Frozen Embryo Transfer Recovery Time?
One of the appealing aspects of FET is the relatively mild "FET recovery" process compared to the egg retrieval phase of IVF. The transfer itself is a quick, minimally invasive procedure, often described as similar to a Pap test.
Immediately After the Transfer:
- Short Rest: You'll typically be asked to lie down for 15-30 minutes immediately after the transfer. Some clinics may recommend longer, but evidence suggests prolonged bed rest isn't beneficial.
- Mild Discomfort: You might experience mild cramping or spotting for a day or two, which is usually normal and related to the catheter passing through the cervix.
- Emotional State: The period immediately following transfer, often called the "two-week wait," can be emotionally challenging. Anxiety and anticipation are common.
In the Days Following:
- Activity Levels: Most doctors recommend resuming light, normal daily activities. Strenuous exercise, heavy lifting, and activities that cause significant jarring (like high-impact running) are usually advised against for a few days to a week.
- Medication: You will continue taking prescribed hormonal medications (estrogen and progesterone) to support the uterine lining and potential early pregnancy. Adherence to this regimen is crucial.
- Avoidance: You might be advised to avoid hot baths, swimming pools, and intercourse for a short period to minimize infection risk, though recommendations vary.
- Monitoring: Some clinics may require follow-up blood tests to check hormone levels before the official pregnancy test.
The waiting period until the pregnancy test (usually 9-14 days post-transfer) can be stressful. It's important to practice self-care, engage in gentle activities, and have a support system. Remember, mild cramping or spotting doesn't necessarily indicate failure, nor does a lack of symptoms confirm pregnancy. Focus on staying positive and healthy during this crucial time.
What Are the Potential Risks and Side Effects of a Frozen Embryo Transfer?
While a Frozen Embryo Transfer is generally a very safe procedure, like any medical intervention, it carries some potential "FET risks" and "FET side effects." It's important to distinguish these from the more significant risks associated with the ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval phase of a fresh IVF cycle, which are largely bypassed in FET.
Common Side Effects (usually mild and related to hormonal medications):
- Cramping and Bloating: Similar to menstrual discomfort, these are common due to hormonal changes and the procedure itself.
- Spotting: Light vaginal bleeding or spotting can occur after the transfer, often due to cervical irritation.
- Breast Tenderness: A common side effect of progesterone medication.
- Mood Swings, Fatigue, Headaches: Hormonal fluctuations can lead to these general symptoms, similar to early pregnancy signs.
Less Common Risks (rare but possible):
- Infection: Though rare, there's a very small risk of infection from the transfer catheter.
- Bleeding: More significant bleeding can occur, but is uncommon.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: If the embryo implants outside the uterus (e.g., in a fallopian tube), it results in an ectopic pregnancy. While FET reduces the risk compared to fresh transfers, it doesn't eliminate it entirely.
- Multiple Pregnancy: The risk depends on the number of embryos transferred. Transferring more than one embryo increases the chance of twins or higher-order multiples, which carries greater risks for both mother and babies.
- Failure to Implant: The most common outcome is that the embryo simply doesn't implant or doesn't develop, leading to a negative pregnancy test. This is not a "risk" of the procedure itself but rather the inherent challenge of fertility treatment.
- Embryo Thawing Failure: While rare with modern vitrification techniques, there's a small chance that an embryo may not survive the thawing process.
Your fertility specialist will discuss these potential risks and side effects with you, ensuring you are fully informed before proceeding with the FET cycle.
How Does Frozen Embryo Transfer Cost Compare Worldwide?
The "Frozen Embryo Transfer cost" is a significant factor for many individuals and couples, especially when considering "fertility treatment abroad." The price can vary dramatically based on the country, clinic, included services, and medication. Generally, Western countries tend to have higher costs compared to popular medical tourism destinations.
Here's a general comparison of FET cycle costs (excluding initial IVF, travel, and accommodation, unless specified):
| Region/Country | Estimated FET Cost (USD) | Notes & Inclusions |
|---|---|---|
| USA/Canada | $4,000 - $8,000+ | Often includes monitoring, thawing, transfer. Medication costs (estrogen/progesterone) are usually separate and can add $500-$1500. |
| Western Europe (e.g., UK, Germany) | $3,500 - $7,000+ | Similar structure to North America; medication often extra. |
| Spain / Czech Republic | $2,500 - $4,500 | Popular for medical tourism. Often competitive packages, sometimes including basic medication or monitoring. |
| Mexico / Turkey | $2,000 - $4,000 | Very attractive for cost savings. Some clinics offer all-inclusive packages for the cycle. |
| India / Thailand | $1,500 - $3,500 | Among the most affordable options, with high-quality care in accredited centers. Medication may be additional. |
Note: These are approximate costs and can vary. Always request a detailed quote from clinics, ensuring it clearly states what is included (e.g., consultation, monitoring scans, thawing, transfer, basic medication, post-transfer follow-up).
Why Consider a Frozen Embryo Transfer Abroad?
For many patients, the decision to undergo a Frozen Embryo Transfer abroad is driven by a compelling combination of practical benefits and personal considerations. This growing trend in "medical tourism fertility" offers several advantages:
- Significant Cost Savings: As seen in the cost comparison, the price of an FET cycle can be considerably lower in popular medical tourism destinations. These savings can make treatment accessible to those for whom it would be financially prohibitive at home, or allow for multiple cycles if needed.
- Access to Advanced Technologies and Specialists: Many international clinics are at the forefront of reproductive medicine, offering cutting-edge techniques and highly experienced specialists. Patients may find access to specific diagnostic tools, advanced lab procedures (like time-lapse imaging), or specialists with particular expertise that might be limited in their home country.
- Shorter Waiting Lists: In some countries, public healthcare systems or popular clinics have long waiting lists for fertility treatments. Traveling abroad can often mean faster access to treatment, reducing the emotional toll of delays.
- Privacy and Anonymity: For some, undergoing such a personal and sensitive treatment away from their local community offers a desired level of privacy and anonymity.
- Comprehensive Packages: Many international clinics cater specifically to medical tourists, offering all-inclusive packages that can cover consultations, the FET procedure, medication, and sometimes even local accommodation and airport transfers, simplifying the logistics.
- Opportunity for a Relaxing Environment: Combining treatment with a 'fertility vacation' can reduce stress. The opportunity to recover in a serene environment, away from daily pressures, can be mentally beneficial during a demanding period.
- Favorable Regulations: Some countries may have different regulations regarding embryo storage, donor options, or specific treatment protocols that might be more aligned with a patient's preferences or needs.
These factors combine to make international FET an increasingly viable and attractive option for individuals and couples worldwide.
Which Countries Offer the Best Value and Quality for FET?
When considering "best countries for FET," patients are typically looking for a balance of high success rates, experienced medical professionals, state-of-the-art facilities, and affordability. Several countries have established themselves as leaders in fertility medical tourism:
- Spain: Renowned for its advanced reproductive technology and liberal laws regarding donor gametes (if needed), Spain has numerous high-quality clinics with excellent success rates. It offers a good balance of quality and affordability compared to other Western European nations.
- Czech Republic: A very popular destination, especially for patients from Western Europe, due to its high-quality care, skilled specialists, and significantly lower costs. Laws are strict regarding anonymity, which appeals to many.
- Mexico: Offering a convenient option for North American patients, Mexico provides high-quality, internationally accredited clinics at a fraction of the cost found in the US. Many clinics are located in tourist-friendly cities.
- Turkey: Known for its modern hospitals and experienced medical staff, Turkey is emerging as a strong contender in fertility tourism. Costs are highly competitive, and care standards are often excellent, particularly in larger cities like Istanbul.
- India: A long-standing medical tourism hub, India offers some of the most affordable FET cycles globally without compromising on quality. Clinics often feature cutting-edge technology and highly trained English-speaking doctors.
- Thailand: Combining advanced medical care with a welcoming tourist environment, Thailand attracts patients from Australia, Asia, and beyond. Its clinics offer competitive pricing and high success rates, often with comprehensive packages.
- Greece and Cyprus: These Mediterranean nations are also gaining popularity for their modern fertility clinics, experienced staff, and more relaxed regulations (e.g., on egg donation age limits) than some other European countries.
When selecting a country, research specific clinics, their success rates (transparently reported), international accreditations (like JCI), and patient reviews to ensure both value and quality.
What Should I Expect When Traveling Abroad for My FET?
"Traveling for FET" involves a systematic process to ensure a smooth and successful experience. Understanding the steps can help manage expectations:
- Initial Consultation (Often Virtual): Your journey typically begins with remote consultations. You'll share your medical history, previous IVF records, and current fertility status with the international clinic via video calls or secure portals. The clinic will assess your eligibility for FET and propose a personalized treatment plan.
- Pre-Travel Preparations:
- Medication Protocol: You'll receive a detailed medication protocol for preparing your uterine lining, which may begin in your home country.
- Travel Logistics: Many clinics or medical tourism facilitators (like PlacidWay) assist with travel arrangements, including flights, airport transfers, and local accommodation that's convenient to the clinic.
- Visa and Documentation: Ensure you have all necessary travel documents, including a valid passport and any required visas for medical treatment.
- Arrival and Local Monitoring:
- Upon arrival, you'll undergo local monitoring at the clinic, including ultrasound scans and blood tests, to track your uterine lining development and hormone levels.
- This phase typically lasts several days to a week, depending on your cycle type (natural vs. programmed).
- Embryo Thawing and Transfer:
- Once your uterine lining is optimally prepared, your frozen embryos will be thawed. The embryologists will assess their viability.
- The actual embryo transfer procedure is quick and typically painless. You'll often be advised to rest for a short period afterward.
- Post-Transfer and Recovery:
- You'll continue with prescribed medications and receive instructions for post-transfer care, including activity restrictions.
- You'll likely stay in the destination for a few more days to ensure stability and potentially for an early pregnancy blood test before returning home.
- Follow-up at Home:
- The clinic will provide clear instructions for follow-up care and testing in your home country.
- Communication channels will remain open for any questions or concerns during the crucial "two-week wait" and beyond.
Expect attentive care, clear communication, and a focus on making your medical journey as stress-free as possible.
How Can I Ensure Safety and Quality for My FET Abroad?
Ensuring "safe IVF abroad" and high-quality care is paramount when choosing an international clinic for your Frozen Embryo Transfer. Diligent research and clear communication are your best tools:
- Check for International Accreditations: Look for clinics that hold international accreditations such as Joint Commission International (JCI). These accreditations signify adherence to rigorous international standards for patient safety and quality of care. Local accreditations are also important.
- Verify Physician Qualifications and Experience: Research the fertility specialists. Ensure they are board-certified, have extensive experience specifically in FET and assisted reproductive technologies, and are members of relevant international professional organizations (e.g., ESHRE, ASRM).
- Inquire About Lab Standards and Technology: The embryology lab is critical for FET success. Ask about their embryo freezing (vitrification) and thawing protocols, the experience of their embryologists, and the technology they use (e.g., time-lapse incubators, advanced embryo selection methods).
- Review Success Rates: Request detailed and transparent success rates for FET, broken down by age groups if possible. Be wary of clinics that promise unrealistic success rates or lack transparency. Compare these rates to reputable national registries if available.
- Read Patient Testimonials and Reviews: Seek out unbiased reviews from other international patients. Websites, forums, and medical tourism platforms can offer insights into patient experiences regarding care quality, communication, and overall satisfaction.
- Ensure Clear Communication: The clinic should have English-speaking staff or readily available translators. Clear and timely communication is vital for understanding your treatment plan, medications, and any potential issues.
- Understand the Full Cost: Get a detailed, itemized quote to avoid hidden fees. Confirm what is included (e.g., medication, monitoring, thawing, transfer, post-procedure follow-up).
- Legal and Ethical Framework: Familiarize yourself with the fertility laws and ethical guidelines of the chosen country, especially concerning embryo storage, donor options, and multiple embryo transfers.
- Medical Tourism Facilitators: Consider using reputable medical tourism facilitators like PlacidWay. They often vet clinics, assist with logistics, and provide an added layer of support and advocacy.
By taking these steps, you can significantly enhance the safety and quality of your FET journey abroad.
What Are Common Patient Success Stories and Outcomes from FET Abroad?
The narratives of patients undergoing "fertility treatment abroad outcomes" often resonate with themes of hope, perseverance, and ultimately, joy. While every individual journey is unique, common threads emerge in the success stories from those who chose FET abroad:
- Achieving Parenthood After Years of Trying: Many patients arrive at international clinics having experienced multiple failed cycles or a lack of accessible options in their home countries. Success abroad often represents the culmination of a long and emotionally draining journey, finally resulting in a positive pregnancy and the birth of a child.
- Affordability Making Dreams Possible: A recurring highlight is how the lower "IVF abroad prices" made treatment financially feasible. For couples who might have given up due to the prohibitive costs at home, international options opened the door to realizing their dream of a family. This affordability often allows for multiple attempts, increasing cumulative success rates.
- Advanced Care and Technology: Patients frequently praise the state-of-the-art facilities and cutting-edge techniques available in leading international clinics. They speak of advanced embryo selection, meticulous lab work, and personalized treatment plans that felt more comprehensive or innovative than what they had access to previously.
- Compassionate and Personalized Care: Many testimonials emphasize the human connection and empathetic approach of the international medical teams. Being treated as individuals, not just numbers, and receiving clear, consistent communication helps alleviate anxiety during a stressful time.
- Seamless Medical Tourism Experience: Success stories often include positive remarks about the well-organized logistics – from virtual consultations to travel arrangements, accommodation, and local support. This holistic approach makes the experience less daunting for international patients.
- The "Fertility Vacation" Aspect: While the primary goal is treatment, the opportunity to combine it with a trip to a new country and recover in a relaxed environment is often cited as a positive. This change of scenery can reduce stress and contribute to a more positive mindset.
- High Success Rates: Patients often share how the transparent and competitive success rates of international clinics encouraged them to travel, and how these rates translated into a successful pregnancy for them.
These stories underscore that for many, seeking FET abroad is not just about a medical procedure, but about finding a more accessible, supportive, and ultimately successful path to building their families.
Take the Next Step with PlacidWay
Ready to explore treatment options abroad? Discover top clinics, compare prices, and get a free quote tailored to your needs with PlacidWay.
Fertility Treatment Abroad, Best Fertility Clinics

.jpeg)





Share this listing