Struggling with High Blood Pressure? Discover Renal Artery Angioplasty Abroad
Living with high blood pressure can be a daily challenge, especially when medications don't seem to work as effectively as they should. You might feel a constant worry about the strain on your heart and kidneys, or perhaps you've already experienced a decline in kidney function that doctors can't quite explain. If you’ve heard terms like "resistant hypertension," "renal artery stenosis," or "blocked kidney arteries," you're likely searching for answers and effective treatment options.
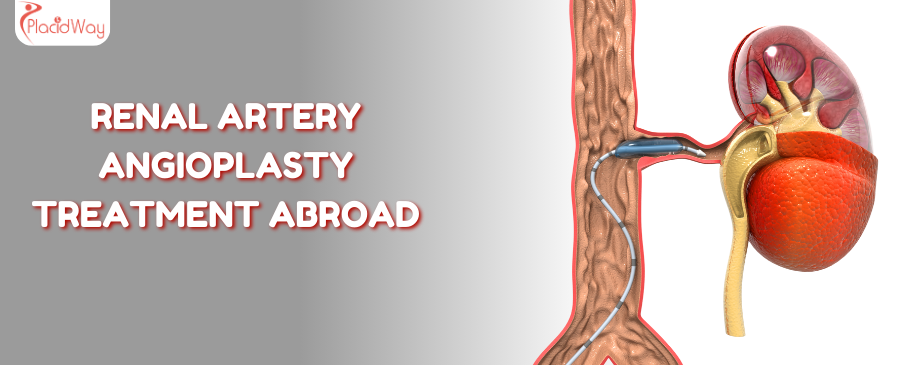
Renal Artery Angioplasty is a specialized, minimally invasive procedure designed to address a common underlying cause of these issues: narrowed or blocked arteries leading to your kidneys. Just like a kink in a garden hose reduces water pressure, a narrowed renal artery restricts blood flow to your kidneys, triggering them to release hormones that dangerously elevate your blood pressure. This procedure aims to reopen these vital pathways, restoring proper blood flow, often leading to better blood pressure control and improved kidney health.
For many, particularly those facing high treatment costs or long waiting lists in their home country, seeking this procedure abroad has become a viable and attractive option. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about renal artery angioplasty, from understanding the symptoms and causes to navigating the process of undergoing treatment in a reputable international clinic. Let's explore how this procedure can offer a new path to better health and well-being.
What are the symptoms of blocked kidney arteries?
Identifying the symptoms of narrowed kidney arteries, medically known as renal artery stenosis, can be tricky because they often mimic other common conditions. However, paying close attention to specific signs can help you and your doctor uncover the root cause. Here are the key indicators people often search for when they suspect a problem with their kidney arteries:
- Resistant Hypertension: This is arguably the most common and significant symptom. It means your high blood pressure is very difficult to control, even with multiple medications. If you're taking three or more antihypertensive drugs, including a diuretic, and your blood pressure remains stubbornly high, it could be a red flag for renal artery stenosis. Patients often search for "resistant high blood pressure causes" or "why won't my blood pressure go down."
- Worsening Kidney Function: A sudden or progressive decline in kidney function, often detected through blood tests (elevated creatinine or reduced eGFR), without a clear explanation can point to a renal artery issue. People might search for "unexplained kidney failure" or "sudden drop in kidney function."
- Fluid Retention and Edema: Restricted blood flow to the kidneys can impair their ability to properly filter waste and fluids, leading to swelling in the legs, ankles, or even around the lungs (pulmonary edema), especially if you also have heart failure. "Swollen ankles high blood pressure" or "fluid retention kidney problems" are common search terms.
- Flash Pulmonary Edema: This is a severe and sudden accumulation of fluid in the lungs, often requiring emergency medical attention. It's a critical sign that your kidneys are not regulating fluid balance effectively due to inadequate blood flow.
- Abdominal Bruit: Sometimes, a doctor can hear a whooshing sound (bruit) with a stethoscope over your abdomen, especially near the kidneys. This sound is caused by turbulent blood flow through a narrowed artery.
- New or Worsening Angina or Heart Failure: The strain of uncontrolled high blood pressure can exacerbate existing heart conditions or even lead to new ones.
If you're experiencing any combination of these symptoms, especially resistant hypertension or unexplained kidney problems, it's crucial to discuss the possibility of renal artery stenosis with your doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve your outcomes.
What causes blockages in the renal arteries?
Understanding the "why" behind narrowed kidney arteries is crucial for both prevention and treatment. There are two main culprits behind renal artery stenosis:
- Atherosclerosis (Hardening of the Arteries): This is by far the most common cause, accounting for about 90% of cases, especially in older adults. Atherosclerosis is a condition where plaque (made of cholesterol, fat, and other substances) builds up inside your arteries, including those leading to your kidneys. Over time, this plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow. It's the same process that causes heart attacks and strokes. Risk factors for atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis include:
- High cholesterol and triglycerides
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Family history of heart disease
Patients often search for "atherosclerosis kidney arteries" or "plaque in kidney arteries treatment."
- Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD): This condition, more common in younger individuals and women, is characterized by abnormal cell growth in the walls of the arteries, causing them to narrow and sometimes bulge in a "string of beads" appearance. The exact cause of FMD is unknown, but genetics may play a role. Unlike atherosclerosis, FMD doesn't involve plaque buildup. It can affect arteries throughout the body, but the renal arteries are a common site. People might search for "fibromuscular dysplasia symptoms" or "FMD kidney artery."
- Less Common Causes: Rarely, other conditions like vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), arterial dissection (a tear in the artery wall), or external compression from tumors can also lead to renal artery narrowing.
Identifying the specific cause is important because it dictates the most effective treatment approach. Your doctor will likely use imaging tests to determine whether atherosclerosis, FMD, or another condition is behind your symptoms.
How does Renal Artery Angioplasty work, and what are the types?
Imagine your kidney artery as a clogged pipe. Renal Artery Angioplasty is like sending a specialized plumbing tool to clear that blockage and restore proper flow. This minimally invasive procedure is performed by an interventional radiologist or cardiologist.
Here's a breakdown of how it generally works and the types available:
The Procedure:
- Access Point: The procedure usually begins with a small incision, typically in your groin (femoral artery), arm, or wrist, through which a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted.
- Guidance: Using X-ray guidance (fluoroscopy) and a contrast dye injected into your bloodstream (which makes blood vessels visible), the doctor carefully navigates the catheter through your arteries until it reaches the narrowed renal artery.
- Balloon Inflation: Once the catheter reaches the blockage, a tiny balloon at its tip is inflated. This inflation compresses the plaque or abnormal tissue against the artery walls, widening the artery and improving blood flow. You might feel some pressure during this step.
- Deflation and Removal: The balloon is then deflated and removed, along with the catheter.
Types of Renal Artery Angioplasty:
- Plain Balloon Angioplasty: This is the most basic form where only the balloon is used to open the artery. It's often effective for certain types of blockages, particularly those caused by fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD), which tends to be less prone to "re-narrowing" after angioplasty alone. Patients often search for "balloon angioplasty kidney" or "how does balloon angioplasty work."
- Renal Artery Angioplasty with Stenting: In many cases, especially when the narrowing is due to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup), the doctor will also place a small, expandable mesh tube called a stent into the artery after balloon inflation. The stent acts as a scaffold to hold the artery open and reduce the chances of it re-narrowing (restenosis) over time. Stents can be bare metal or drug-eluting (coated with medication to prevent cell growth). "Renal artery stenting procedure" and "stent for kidney artery blockage" are common search terms related to this.
The choice between plain angioplasty and stenting depends on several factors, including the cause of the narrowing, its location, severity, and the individual patient's anatomy. Your medical team will discuss the best approach for your specific situation.
Am I a candidate for renal artery angioplasty?
Deciding if renal artery angioplasty is right for you involves a thorough evaluation by a medical specialist. It's not a procedure for every case of high blood pressure or kidney issues. Doctors look for specific criteria, and patients often search for "who needs renal artery angioplasty" or "eligibility for renal angioplasty."
Here are the common scenarios where angioplasty might be recommended:
- Resistant Hypertension: If your high blood pressure remains uncontrolled despite taking a regimen of three or more antihypertensive medications (one of which is a diuretic), and tests confirm significant renal artery stenosis (typically greater than 70% narrowing).
- Worsening Kidney Function: Patients experiencing a progressive decline in kidney function that is directly attributable to severe renal artery stenosis may benefit. The goal here is to preserve or improve kidney function.
- Recurrent Flash Pulmonary Edema: This life-threatening condition, where fluid rapidly builds up in the lungs, can be a direct consequence of severe renal artery stenosis. Angioplasty can be a crucial intervention in such cases.
- Intolerance to Medications: In rare cases, if you cannot tolerate the side effects of blood pressure medications and have significant stenosis, angioplasty might be considered.
- Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD): Patients, especially younger ones, with symptomatic renal artery stenosis caused by FMD are generally excellent candidates for plain balloon angioplasty, often with very good long-term results.
Who might NOT be a candidate?
- Mild Stenosis: If the narrowing is not severe (e.g., less than 50-60%) and you don't have significant symptoms, medication management is usually the preferred approach.
- Stable Kidney Function with Controlled BP: If your blood pressure is well-controlled with medication and your kidney function is stable, even with some stenosis, the risks of angioplasty may outweigh the potential benefits.
- Extensive Kidney Damage: If the kidney has already suffered irreversible damage from long-standing, severe stenosis, restoring blood flow may not lead to significant improvement in function.
- Other Medical Conditions: Certain severe underlying health issues might make the procedure too risky.
Your doctor will conduct various diagnostic tests, including duplex ultrasound, CT angiography, or MR angiography, to confirm the presence and severity of renal artery stenosis and determine if angioplasty is the best course of action for your specific health situation.
What is the typical recovery time after renal artery angioplasty?
One of the appealing aspects of renal artery angioplasty, being a minimally invasive procedure, is its relatively quick recovery time compared to open surgery. Patients often search for "renal artery angioplasty recovery" or "life after renal angioplasty" to understand what to expect.
Immediate Post-Procedure:
- Hospital Stay: Most patients will spend one to two nights in the hospital for observation. This allows the medical team to monitor the access site for bleeding and ensure your blood pressure and kidney function are stable.
- Bed Rest: You'll typically need to lie flat for several hours after the procedure, especially if the access site was in your groin, to prevent bleeding.
- Pain Management: You might experience some mild discomfort or bruising at the access site, which can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
First Few Days (at Home):
- Activity Restrictions: For about 3-7 days, you'll be advised to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, and bending at the waist to protect the access site. Walking and light daily activities are usually encouraged.
- Monitoring: Continue to monitor the access site for any signs of infection (redness, swelling, discharge) or excessive bruising/bleeding.
- Medication Adjustments: Your doctor will likely adjust your blood pressure medications as needed, as many patients experience improved blood pressure control soon after the procedure. You may also be prescribed anti-platelet medication (like aspirin) to prevent blood clots on the stent, if one was placed.
Longer Term (Weeks to Months):
- Gradual Return to Normal: Most people can return to their normal daily routines, including work, within 1-2 weeks, depending on their overall health and the nature of their work.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up with your doctor is essential. This will include monitoring your blood pressure, kidney function tests, and possibly follow-up imaging (like ultrasound) to check the treated artery.
- Lifestyle Changes: To maintain the benefits of the angioplasty, it's crucial to continue with heart-healthy lifestyle changes: a balanced diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing underlying conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol.
It's important to remember that individual recovery times can vary based on your overall health, the complexity of the procedure, and any pre-existing conditions. Always follow your doctor's specific post-procedure instructions carefully.
What are the risks and side effects of renal artery angioplasty?
Like any medical procedure, renal artery angioplasty carries potential risks and side effects, though serious complications are rare. It's important to be aware of these so you can make an informed decision and know what to look out for during recovery. Patients often search for "risks of renal artery angioplasty" or "complications of kidney artery stent."
Common and Minor Side Effects:
- Bruising and Soreness at the Access Site: It's common to have some bruising, swelling, or tenderness where the catheter was inserted (e.g., in the groin). This typically resolves within a few days.
- Mild Discomfort: You might feel a brief, mild discomfort when the balloon is inflated.
Potential Risks and Complications (Less Common):
- Bleeding: There's a risk of bleeding at the catheter insertion site, which can range from a small bruise to a more significant hematoma (collection of blood).
- Artery Damage: In rare cases, the catheter or balloon can injure the artery wall, leading to a tear (dissection), perforation, or blockage. This might require further intervention.
- Kidney Damage (from Contrast Dye): The contrast dye used during the procedure can sometimes temporarily or, rarely, permanently impair kidney function, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney disease. Your medical team will take precautions, like using minimal dye and ensuring you are well-hydrated.
- Allergic Reaction: Some people may have an allergic reaction to the contrast dye, medications, or anesthesia used during the procedure.
- Restenosis (Re-narrowing): Despite the procedure, the treated artery can re-narrow over time, requiring another intervention. This risk is higher with plain balloon angioplasty for atherosclerotic disease, which is why stents are often used.
- Cholesterol Embolization: In some cases, plaque loosened during the procedure can travel to smaller blood vessels, potentially affecting the kidneys or other organs.
- Blood Clot Formation: A blood clot can form at the site of the angioplasty or on the stent, potentially blocking blood flow. This is why anti-platelet medications are often prescribed.
- Infection: Any invasive procedure carries a small risk of infection at the access site.
Your medical team will carefully assess your individual risk factors and discuss them with you before the procedure. They will also take all necessary precautions to minimize these risks and ensure your safety throughout the process.
How much does Renal Artery Angioplasty cost worldwide?
The cost of renal artery angioplasty can be a major factor for many patients, especially those without comprehensive insurance coverage or facing high deductibles in their home countries. This is a primary driver for people searching for "cost of renal artery angioplasty," "renal angioplasty price abroad," or "affordable kidney artery treatment."
Prices fluctuate widely based on geographical location, the hospital's reputation, the surgeon's fees, the type of angioplasty (with or without stent), the duration of hospital stay, and the inclusion of pre/post-operative care.
Here's a general cost comparison to give you an idea:
| Country | Estimated Cost Range (USD) | Notes on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| United States | $25,000 - $50,000+ | Highest costs globally; varies significantly by state, hospital, and insurance coverage. Includes surgeon fees, facility fees, anesthesia. |
| United Kingdom | £15,000 - £30,000 ($19,000 - $38,000+) | NHS may cover it, but private care is expensive. Wait times for elective procedures can be long. |
| India | $5,000 - $12,000 | Highly competitive prices with world-class facilities and experienced doctors. Popular medical tourism destination. |
| Mexico | $6,000 - $15,000 | Attractive for North American patients due to proximity and lower costs. Good quality hospitals near the border. |
| Thailand | $7,000 - $14,000 | Known for excellent medical infrastructure, highly trained staff, and a pleasant recovery environment. |
| Turkey | $6,000 - $13,000 | Emerging medical tourism hub with modern hospitals and competitive pricing. |
Please note: These are estimated ranges and can change. Always get a personalized quote that includes all aspects of your treatment. Factors like the type of stent (drug-eluting vs. bare metal), the length of hospital stay, and specific pre/post-operative tests can influence the final cost.
Many medical tourism facilitators, like PlacidWay, can help you obtain transparent quotes from multiple international hospitals, ensuring you understand exactly what's included.
Why consider renal artery angioplasty in another country?
The decision to seek medical treatment outside your home country, often referred to as "medical tourism," is growing in popularity, especially for procedures like renal artery angioplasty. For many, it's not just an option but a necessity. Patients often search for "medical tourism renal angioplasty," "treatment abroad for kidney artery disease," or "benefits of overseas medical treatment." Here's why:
- Significant Cost Savings: This is often the primary motivator. As seen in the cost comparison table, the price difference for the same procedure can be staggering. Patients can save anywhere from 50% to 80% on costs compared to Western countries like the US or UK, even when factoring in travel and accommodation.
- Shorter Waiting Times: In some countries, public healthcare systems can have long waiting lists for elective or even semi-urgent procedures. Traveling abroad allows patients to bypass these delays and receive timely treatment, which can be critical for conditions affecting kidney function.
- Access to Advanced Technology and Specialized Care: Many international hospitals in medical tourism hubs boast state-of-the-art equipment and highly trained specialists, some of whom have received education and training in leading Western institutions. These facilities often offer cutting-edge treatments that might be unavailable or difficult to access elsewhere.
- High-Quality Standards and Accreditation: Reputable medical tourism destinations have hospitals that are internationally accredited (e.g., JCI - Joint Commission International), ensuring they meet stringent global standards for patient safety and quality of care.
- Privacy and Anonymity: For some, undergoing a medical procedure away from their home country offers a level of privacy and anonymity that they value during a vulnerable time.
- Opportunity for a "Medical Vacation": While the primary goal is treatment, many patients combine their medical journey with a recovery period in an exotic or peaceful location, often at a lower overall cost than their domestic treatment alone.
- Personalized Attention: Due to the competitive nature of medical tourism, many international clinics offer a highly personalized patient experience, with dedicated patient coordinators and comprehensive support services.
Choosing to go abroad requires careful research and planning, but for many, the benefits of cost, quality, and accessibility make it a compelling choice for renal artery angioplasty.
Which countries offer the best value for renal artery angioplasty?
When searching for "best countries for renal angioplasty" or "top medical tourism destinations kidney treatment," several nations consistently rise to the top for offering excellent medical care at competitive prices. These countries have invested heavily in their healthcare infrastructure and cater specifically to international patients.
Here are some of the leading destinations for renal artery angioplasty, known for balancing quality and affordability:
- India: Renowned as a global medical tourism powerhouse, India offers state-of-the-art hospitals, highly qualified cardiologists and interventional radiologists, and JCI-accredited facilities. The cost savings are substantial, often providing comprehensive packages that include accommodation and transfers.
- Thailand: Known for its exceptional hospitality and advanced medical facilities, Thailand boasts world-class hospitals, particularly in Bangkok, with English-speaking staff and luxurious patient accommodations. The quality of care is on par with Western standards, at a fraction of the cost.
- Mexico: A popular choice for patients from North America due to its geographical proximity, Mexico offers high-quality medical care in modern hospitals, particularly in cities like Tijuana, Cancun, and Monterrey. The cost savings are significant, and travel is relatively easy.
- Turkey: Positioned as a bridge between Europe and Asia, Turkey has emerged as a strong medical tourism contender. It features numerous JCI-accredited hospitals with cutting-edge technology and experienced medical professionals, particularly in Istanbul and Ankara, all at very competitive prices.
- Malaysia: With a focus on patient-centric care, Malaysia's medical facilities are highly regarded. It offers a blend of affordability, quality, and a comfortable recovery environment, particularly in cities like Kuala Lumpur and Penang.
- Costa Rica: For those seeking a tranquil environment for recovery, Costa Rica provides excellent medical care in modern facilities, alongside beautiful natural surroundings, often favored by patients from the Americas.
When choosing a destination, it’s essential to look beyond just the price. Consider factors like:
- Hospital Accreditation: Look for international accreditations like JCI.
- Physician Qualifications: Research the experience and credentials of the interventional cardiologist or radiologist.
- Patient Reviews and Testimonials: Read about other patients' experiences.
- Language and Communication: Ensure there will be no language barrier.
- Post-Procedure Care: Understand what follow-up care is provided.
Engaging with a medical tourism facilitator can help streamline this research and ensure you select a reputable and suitable facility for your needs.
What should I expect when traveling for renal artery angioplasty abroad?
Traveling for a medical procedure like renal artery angioplasty abroad involves a structured process to ensure safety, comfort, and the best possible outcome. Patients often search for "medical travel planning renal angioplasty," "how to plan medical trip abroad," or "logistics of overseas medical treatment." Here’s a general roadmap of what to expect:
Phase 1: Research and Planning
- Initial Inquiry: You'll typically start by contacting a medical tourism facilitator (like PlacidWay) or directly reaching out to international hospitals.
- Medical Records Review: You'll be asked to send your medical records, test results, and doctor's reports. The overseas medical team will review these to determine if you're a suitable candidate and provide a preliminary treatment plan and quote.
- Consultation: Many facilities offer virtual consultations with the specialist who would perform your procedure, allowing you to ask questions and build confidence.
- Transparent Quote: Expect a detailed quote covering the procedure, hospital stay, medication, and sometimes accommodation and transfers. Clarify what's included and what's not.
- Choosing Your Destination and Clinic: Based on the quotes, specialist profiles, and location preferences, you'll make your informed decision.
Phase 2: Travel Arrangements
- Travel Logistics: Your facilitator can assist with booking flights, arranging visas (if needed), and securing accommodation for yourself and any accompanying family members.
- Pre-Departure Information: You'll receive comprehensive information regarding your travel itinerary, what to pack, local customs, and emergency contacts.
Phase 3: Arrival and Pre-Procedure
- Airport Welcome: Many services include airport pickup and transfer to your accommodation or directly to the hospital.
- Hospital Admission and Tests: Upon arrival at the hospital, you'll undergo a thorough medical evaluation, including blood tests, imaging, and a final consultation with your medical team.
- Pre-Operative Instructions: You'll receive clear instructions regarding diet, medications, and preparation for the angioplasty.
Phase 4: The Procedure and Recovery
- The Angioplasty: The procedure itself is typically short (1-2 hours) and performed under local anesthesia with sedation.
- Hospital Stay: As mentioned, expect 1-2 nights in the hospital for observation and initial recovery.
- Local Support: A patient coordinator or interpreter will often be available to assist with communication and any needs during your hospital stay.
- Outpatient Recovery: Once discharged, you'll typically spend a few days to a week recovering in your accommodation before being cleared for travel home.
Phase 5: Post-Procedure and Follow-up
- Post-Op Check-ups: You'll have follow-up appointments with your surgeon before you depart to ensure your recovery is progressing well.
- Medical Reports: You'll receive all your medical records and discharge summaries to share with your local doctor back home.
- Remote Follow-up: Many clinics offer remote follow-up or support for questions that may arise once you're back home.
Working with a reputable medical tourism facilitator can greatly simplify this process, providing guidance and support every step of the way, making your medical journey as stress-free as possible.
Take the Next Step with PlacidWay
Ready to explore treatment options abroad? Discover top clinics, compare prices, and get a free quote tailored to your needs with PlacidWay.
Vascular Surgery Abroad | Best Vascular Treatment Center









Share this listing