Explore the Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis in Germany
"Stem cell therapy in Germany helps in osteoarthritis treatment by utilizing the regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties of stem cells, often mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), to potentially repair damaged cartilage, reduce pain, and improve joint function."

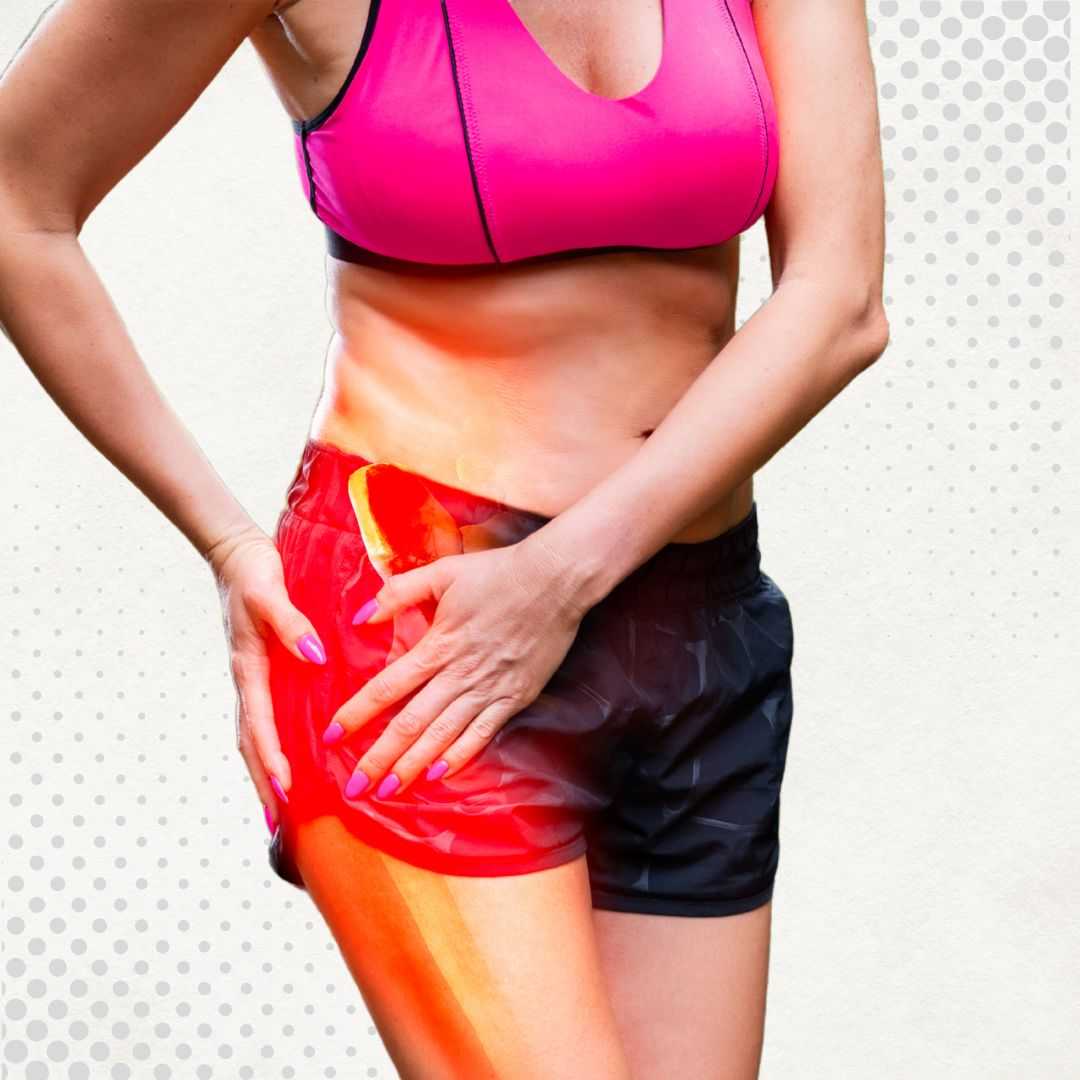
Osteoarthritis, a widespread chronic condition, primarily affects the cartilage in joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. For many years, conventional treatments have focused on managing symptoms rather than addressing the underlying cause. However, advancements in regenerative medicine, particularly stem cell therapy, are offering new hope. Germany has emerged as a leading country in the field of stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis, providing cutting-edge treatments that aim to harness the body's natural healing mechanisms to repair damaged tissues and reduce inflammation. This innovative approach seeks to improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from this debilitating joint disease.
What is Osteoarthritis and How Does it Affect Joints?
"Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling, primarily affecting the weight-bearing joints."
Osteoarthritis, often referred to as "wear and tear" arthritis, is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage on the ends of your bones wears down over time. Cartilage is a firm, slippery tissue that enables nearly frictionless joint motion. In osteoarthritis, this cartilage becomes rough and eventually erodes, causing bones to rub directly against each other. This friction leads to pain, inflammation, swelling, and reduced flexibility in the affected joint. The progression of osteoarthritis can significantly impair a person's ability to perform daily activities, impacting their overall quality of life. Common joints affected include the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
What are Stem Cells and Their Role in Regeneration?
"Stem cells are unique cells with the ability to self-renew and differentiate into various specialized cell types, playing a crucial role in the body's natural repair and regeneration processes."
Stem cells are often called the body's raw materials. They are undifferentiated cells that have two key characteristics: first, they can divide and produce more stem cells (self-renewal); and second, they can develop into many different cell types in the body (differentiation). In the context of regenerative medicine, these properties are invaluable. For osteoarthritis treatment, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are particularly relevant due to their potential to differentiate into cartilage-producing cells (chondrocytes), bone cells (osteoblasts), and fat cells (adipocytes). Beyond differentiation, stem cells also have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties, meaning they can help reduce inflammation and promote a healing environment within the joint.
How Does Stem Cell Therapy Specifically Target Osteoarthritis in Germany?
"Stem cell therapy in Germany primarily targets osteoarthritis by injecting autologous stem cells (usually Mesenchymal Stem Cells from bone marrow or fat) directly into the affected joint to promote cartilage regeneration, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain."
In Germany, stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis typically involves harvesting stem cells from the patient's own body, most commonly from bone marrow (Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate, BMAC) or adipose tissue (fat). These autologous stem cells are then processed to concentrate the mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Once processed, the concentrated stem cells are precisely injected into the osteoarthritic joint. The goal is for these MSCs to either differentiate into new cartilage cells or, more commonly, to exert their therapeutic effects through paracrine signaling. This means they release growth factors and anti-inflammatory molecules that encourage the body's own repair mechanisms, reduce pain, and slow down cartilage degradation. German clinics often employ advanced imaging techniques to ensure the precise placement of the stem cells into the damaged area.
What Types of Stem Cells Are Used for Osteoarthritis Treatment in Germany?
"For osteoarthritis treatment in Germany, the primary type of stem cells used are Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), typically harvested from the patient's own bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue."
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into various cell types, including chondrocytes (cartilage cells), osteoblasts (bone cells), and adipocytes (fat cells). Their multipotent nature and immunomodulatory properties make them ideal candidates for osteoarthritis treatment.
- Bone Marrow-Derived MSCs (BM-MSCs): These are harvested from the patient's bone marrow, usually from the hip bone. BM-MSCs have a long history of study in regenerative medicine and are known for their ability to promote cartilage and bone repair.
- Adipose-Derived MSCs (AD-MSCs): These are obtained from the patient's own fat tissue, often through a liposuction-like procedure. AD-MSCs are abundant and relatively easy to harvest, making them a popular choice.
In Germany, the focus is generally on using autologous stem cells to minimize the risk of immune rejection or disease transmission, aligning with stringent safety regulations.
What Are the Potential Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis?
"Potential benefits of stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis include pain reduction, improved joint function and mobility, potential for cartilage regeneration, and a reduced need for more invasive surgeries like joint replacement."
Stem cell therapy aims to go beyond just managing symptoms. The proposed benefits are:
- Pain Reduction: Many patients experience a significant decrease in joint pain, which can lead to a reduced reliance on pain medications. This is often attributed to the anti-inflammatory effects of stem cells.
- Improved Mobility and Function: By reducing pain and promoting healing, stem cell therapy can help restore a greater range of motion and overall joint function, making daily activities easier.
- Cartilage Regeneration: While complete regrowth of original hyaline cartilage is challenging, stem cells may promote the formation of new tissue that acts as a scaffold and provides support to the joint.
- Reduced Inflammation: MSCs possess potent anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to calm the inflamed joint environment characteristic of osteoarthritis.
- Delay or Avoidance of Surgery: For some patients, stem cell therapy may offer an alternative to surgical interventions, such as total joint replacement, particularly in the earlier stages of the disease.
These benefits can vary from person to person, and the long-term effects are still under ongoing research.
What Does the Stem Cell Therapy Procedure in Germany Involve?
"The stem cell therapy procedure in Germany typically involves a consultation and diagnostic imaging, stem cell harvesting (from bone marrow or fat), processing to concentrate the MSCs, and then precise injection of the stem cells into the affected joint, often guided by imaging."
The procedure generally follows several steps:
- Initial Consultation and Diagnostics: A comprehensive evaluation is conducted, including a medical history review, physical examination, and advanced imaging such as MRI or X-rays to assess the extent of cartilage damage and overall joint health.
- Stem Cell Harvesting: Depending on the chosen source, either a small amount of bone marrow is extracted from the patient's hip bone (bone marrow aspiration) or adipose tissue is collected through a mini-liposuction procedure. Both procedures are typically performed under local anesthesia.
- Processing and Concentration: The harvested tissue is then processed in a specialized laboratory to isolate and concentrate the mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). This often involves centrifugation, which separates the stem cells from other components.
- Injection: The concentrated stem cell solution is then carefully injected directly into the affected joint. This injection is often guided by ultrasound or fluoroscopy to ensure accurate placement of the stem cells into the damaged area.
- Post-Procedure Care: Patients are usually monitored for a short period after the injection. Post-procedure instructions may include rest, gentle movement, and avoidance of strenuous activities for a certain time. Physical therapy may also be recommended as part of the recovery process to optimize results.
How Long Does the Recovery Process Take After Stem Cell Therapy?
"The recovery process after stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis is typically minimal, with most patients experiencing mild soreness for a few days, and a gradual improvement in symptoms over several weeks to months as the stem cells work."
Unlike surgical interventions, stem cell therapy is a minimally invasive procedure, leading to a relatively quick initial recovery. Patients can usually return to light activities within a few days. Some common post-injection experiences include:
- Immediate Post-Procedure: Mild pain, swelling, or bruising at the injection site and the harvest site (if autologous cells were used). These symptoms typically subside within a few days.
- Weeks 1-4: Patients are often advised to avoid strenuous activities to allow the stem cells to begin their work in a calm environment. Gentle rehabilitation exercises may be introduced.
- Months 1-6: This is when patients typically start to notice more significant improvements in pain and function. The stem cells continue to exert their regenerative and anti-inflammatory effects over this period. The full benefits may take several months to become apparent.
Individual recovery times can vary based on the patient's overall health, the severity of their osteoarthritis, and adherence to post-treatment guidelines.
Are There Any Risks or Side Effects Associated with Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis?
"While generally considered safe, stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis carries minimal risks, including temporary pain or swelling at the injection site, infection, or, rarely, an allergic reaction; serious adverse events are uncommon, especially with autologous stem cells."
As with any medical procedure, there are potential risks, though those associated with autologous stem cell therapy are typically low:
- Injection Site Reactions: The most common side effects are temporary pain, swelling, or bruising at the site of injection or where the stem cells were harvested (e.g., hip for bone marrow).
- Infection: While rare, there's a small risk of infection at the injection site. This risk is minimized by performing the procedure in a sterile environment.
- Bleeding: Minimal bleeding can occur at the harvest or injection site.
- Nerve Damage: Extremely rare, but possible if a nerve is inadvertently punctured during the injection.
- Lack of Efficacy: Not every patient responds to stem cell therapy in the same way, and some may not experience significant improvement.
- Tumor Formation: This is a theoretical concern, particularly with certain types of stem cells or if cells are extensively manipulated or cultured outside the body; however, with adult mesenchymal stem cells derived directly from the patient and minimally processed, the risk is considered extremely low. German regulations are strict regarding the handling of stem cells to ensure patient safety.
It's crucial for patients to discuss all potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider.
How Much Does Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis Cost in Germany?
"The cost of stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis in Germany typically ranges from €6,500 to €25,000, varying based on the clinic, the type and source of stem cells used, the severity of the osteoarthritis, and the number of joints treated."
The price of stem cell therapy can be a significant consideration. In Germany, several factors influence the final cost:
- Clinic Reputation and Location: Highly specialized clinics or those in major cities might have higher fees.
- Type of Stem Cells: While autologous MSCs from bone marrow or adipose tissue are common, the exact harvesting and processing methods can influence cost.
- Severity of Osteoarthritis: More advanced cases requiring additional procedures or higher cell counts might incur higher costs.
- Number of Joints Treated: Treating multiple joints simultaneously will naturally increase the overall price.
- Included Services: The total cost often includes the initial consultation, diagnostic tests, the stem cell harvesting and processing, the injection procedure, and sometimes follow-up appointments. Additional costs may include flights, accommodation, and rehabilitation.
Patients should request a detailed cost breakdown from the clinic before proceeding with treatment.
What is the Success Rate of Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis in Germany?
"The success rate of stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis in Germany is promising, with many patients reporting significant improvements in pain and function; however, it varies depending on individual factors, the severity of the condition, and the specific treatment protocol."
While not a guaranteed cure, numerous studies and clinical experiences in Germany suggest positive outcomes for stem cell therapy in osteoarthritis. Success is often measured by:
- Pain Reduction: A significant decrease in reported pain levels.
- Improved Functionality: Enhanced ability to perform daily activities and increased range of motion in the affected joint.
- Reduced Need for Pain Medication: Patients relying less on painkillers.
- Delay of Joint Replacement Surgery: For some, stem cell therapy can postpone or even eliminate the need for more invasive surgical options.
It's important to understand that individual results can vary. Factors like age, overall health, the stage of osteoarthritis, and adherence to post-treatment recommendations can all influence the outcome. German clinics often emphasize a personalized approach to maximize potential benefits for each patient.
How Does German Regulation Ensure the Safety and Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy?
"German regulation ensures the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy through stringent oversight by bodies like the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) and the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, which authorize and monitor stem cell therapies, ensuring high scientific and ethical standards."
Germany has a robust and well-defined regulatory framework for stem cell therapy, which is a significant reason for its reputation in the field. Key aspects include:
- Strict Authorization and Monitoring: The use of stem cell therapies is tightly regulated, requiring specific authorizations and ongoing monitoring by federal agencies. This ensures that treatments are performed in accredited facilities with qualified personnel.
- Focus on Autologous Treatments: German regulations often favor the use of autologous stem cells (from the patient's own body) over allogeneic (donor) cells to minimize immunological risks.
- Quality Control: Clinics must adhere to strict quality control standards for stem cell processing, handling, and administration, ensuring the purity and viability of the cells.
- Ethical Guidelines: Comprehensive ethical guidelines are in place to protect patient rights and ensure responsible conduct of research and clinical application.
- Emphasis on Research and Evidence: While offering cutting-edge treatments, Germany also maintains a strong commitment to scientific research and evidence-based medicine, ensuring that treatments are continuously evaluated for their safety and efficacy.
These regulations help instill confidence in patients seeking stem cell therapy in Germany.
What Should I Consider When Choosing a Clinic for Stem Cell Therapy in Germany?
"When choosing a stem cell therapy clinic in Germany, consider the clinic's accreditation and certifications, the experience and specialization of the medical team, the type of stem cells used, the transparency of costs, and patient testimonials or success stories."
Selecting the right clinic is crucial for a successful stem cell therapy experience. Here are key factors to consider:
- Accreditation and Licensing: Ensure the clinic is officially licensed and accredited by German health authorities. This indicates adherence to high standards of care.
- Medical Team Expertise: Look for clinics with experienced doctors and specialists in regenerative medicine and orthopedics, particularly those with a proven track record in osteoarthritis treatment.
- Type of Stem Cells and Procedure: Confirm that the clinic uses autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and inquire about their specific harvesting and processing methods. A transparent explanation of the entire procedure is essential.
- Diagnostic Capabilities: A reputable clinic will utilize advanced diagnostic tools to accurately assess your condition before recommending stem cell therapy.
- Transparency in Costs: Obtain a clear and detailed breakdown of all costs involved, including the procedure, consultations, diagnostics, and follow-up care, to avoid any hidden fees.
- Patient Support and Communication: Good clinics offer comprehensive patient support, including assistance with travel arrangements, language services, and clear communication throughout the treatment process.
- Patient Testimonials and Outcomes: While individual results vary, testimonials and reported outcomes can provide insight into the clinic's approach and patient satisfaction.
Can Stem Cell Therapy Help Prevent Joint Replacement Surgery?
"Stem cell therapy may help prevent or delay joint replacement surgery by potentially regenerating damaged cartilage, reducing inflammation, and improving joint function, especially in the earlier stages of osteoarthritis."
For many individuals suffering from osteoarthritis, joint replacement surgery is often considered a last resort. Stem cell therapy offers a less invasive alternative that aims to address the root cause of the problem. By promoting cartilage repair and reducing inflammation within the joint, stem cell therapy can potentially:
- Slow Disease Progression: By supporting the body's natural healing, stem cells may help slow down the further degeneration of cartilage.
- Improve Quality of Life: Reduced pain and improved mobility can significantly enhance a patient's daily life, making the need for a major surgical procedure less immediate or even unnecessary.
- Maintain Natural Joint Function: Unlike a prosthetic joint, stem cell therapy works with the body's natural structures, aiming to preserve the existing joint and its natural mechanics for as long as possible.
While stem cell therapy is not a guaranteed preventative measure for everyone, especially those with very advanced osteoarthritis, it presents a viable option for many patients seeking to avoid or delay joint replacement surgery.
What Research and Clinical Trials are Happening in Germany for Osteoarthritis Stem Cell Therapy?
"Germany is at the forefront of stem cell research and clinical trials for osteoarthritis, focusing on optimizing stem cell dosages, delivery methods, and long-term efficacy, with studies involving mesenchymal stem cells from various sources."
German medical institutions and research centers are actively involved in advancing the field of stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis. This includes:
- Optimizing Protocols: Researchers are continuously working to refine the best methods for harvesting, processing, and delivering stem cells to maximize their therapeutic effect. This involves investigating optimal cell numbers, injection techniques, and potential adjunct therapies.
- Understanding Mechanisms: Studies are delving deeper into the precise mechanisms by which stem cells exert their beneficial effects, whether through direct differentiation, paracrine signaling (releasing healing factors), or modulating the immune response.
- Long-Term Outcomes: Ongoing clinical trials are tracking patients over extended periods to assess the long-term safety, durability of effects, and overall impact on osteoarthritis progression.
- Exploring New Sources: While bone marrow and adipose tissue are common, research also explores other potential stem cell sources and formulations, including the use of exosomes and growth factors derived from stem cells.
- Collaboration: German researchers often collaborate internationally, contributing to a global understanding and advancement of regenerative medicine for osteoarthritis.
This continuous research ensures that stem cell therapy in Germany remains at the cutting edge of medical innovation.
Is Stem Cell Therapy a Cure for Osteoarthritis?
"Stem cell therapy is not considered a definitive cure for osteoarthritis, but rather a regenerative treatment that aims to significantly alleviate symptoms, improve joint function, and potentially slow down the progression of cartilage degeneration."
It's important to have realistic expectations about stem cell therapy. While it offers significant promise and can lead to substantial improvements for many patients, it is not currently understood as a "cure" that completely reverses all damage or guarantees a permanent solution to osteoarthritis. Instead, it functions as a powerful regenerative treatment that:
- Modulates the Disease: It helps to create a healthier environment within the joint, reducing inflammation and promoting the body's natural repair processes.
- Improves Symptoms: The primary goal is to reduce pain, stiffness, and swelling, leading to better quality of life.
- Potential for Tissue Repair: While complete regeneration of original hyaline cartilage is complex, stem cells can facilitate the formation of new tissue that provides cushioning and support.
- Delays Progression: By addressing underlying mechanisms of the disease, stem cell therapy can potentially slow down the further degeneration of the joint over time.
Therefore, patients should view stem cell therapy as a highly effective management and regenerative strategy rather than an outright cure.
What is the Eligibility Criteria for Stem Cell Therapy in Germany?
"The eligibility criteria for stem cell therapy in Germany typically involve a diagnosis of osteoarthritis, good general health, realistic expectations, and an evaluation by a specialist to determine if the patient is a suitable candidate for the specific stem cell protocol."
Eligibility for stem cell therapy is determined on a case-by-case basis after a thorough medical evaluation. While criteria can vary slightly between clinics and specific protocols, general considerations include:
- Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis: Patients must have a confirmed diagnosis of osteoarthritis, often supported by imaging studies. The severity of the condition may influence suitability.
- Overall Health: Patients should be in generally good health, without active infections, certain autoimmune diseases, or specific cancers that might contraindicate the procedure.
- Realistic Expectations: Patients should understand that stem cell therapy is a regenerative treatment aiming for improvement, not a guaranteed cure.
- Absence of Contraindications: Certain medications (like blood thinners, which may need to be temporarily stopped), or specific joint conditions might be contraindications.
- Age: While there is no strict age limit, older patients might have fewer stem cells available, which can be a factor in autologous treatments. However, many older adults successfully undergo the procedure.
- Previous Treatments: The response to prior conservative treatments (like physical therapy, medication, or PRP injections) may also be considered.
A specialized medical team in Germany will conduct a comprehensive assessment to determine if stem cell therapy is the most appropriate and beneficial option for each individual patient.
Are There Any Long-Term Side Effects of Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis?
"Current research on stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis suggests that long-term side effects are rare, especially with autologous mesenchymal stem cells, with most reported adverse events being mild and temporary, such as localized pain or swelling."
The long-term safety profile of stem cell therapy, particularly using autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), is a significant focus of ongoing research and clinical monitoring in Germany and worldwide. To date, substantial evidence points to a generally favorable safety record:
- Minimal Serious Risks: Serious long-term adverse events, such as tumor formation or severe immune reactions, have been exceedingly rare in well-regulated clinical settings using autologous adult MSCs.
- Transient Side Effects: The most common "side effects" observed are short-term and related to the injection procedure itself, such as temporary pain, bruising, or swelling at the treatment site, which typically resolve within days or weeks.
- No Evidence of Systemic Issues: Studies generally do not indicate long-term systemic health issues arising from localized stem cell injections for osteoarthritis.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Clinics in Germany often conduct follow-up assessments to monitor patient progress and identify any potential long-term issues, contributing to the growing body of knowledge on the therapy's safety.
While research is ongoing and the field is constantly evolving, the current understanding suggests that autologous stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis carries a low risk of significant long-term side effects.
What is the Typical Timeline for Results After Stem Cell Therapy?
"The typical timeline for results after stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis usually involves initial improvements in pain and comfort within a few weeks, with more significant and sustained benefits in pain reduction and functional improvement becoming noticeable over 3 to 6 months, and potentially continuing for up to a year."
The effects of stem cell therapy are not instantaneous because the treatment relies on the body's natural healing and regenerative processes. Here's a general timeline:
- Week 1-4: Patients may experience some initial soreness or discomfort from the injection. Some might start to notice a subtle reduction in pain as inflammation begins to subside.
- Month 1-3: This period often marks the beginning of more noticeable improvements. Pain relief typically becomes more significant, and there might be a gradual increase in joint mobility and reduction in stiffness. The stem cells are actively working to modulate the environment and initiate repair processes.
- Month 3-6: Many patients report their most substantial improvements during this phase. Joint function is often considerably better, and pain levels are significantly reduced. The regenerative effects of the stem cells are more apparent.
- Month 6-12 and Beyond: The benefits can continue to evolve and stabilize. Some patients experience sustained relief for a year or longer, and the therapy may help to slow the progression of osteoarthritis. The longevity of results can vary by individual.
It's important to remember that these are general timelines, and individual responses can differ based on the severity of the osteoarthritis, the patient's overall health, and adherence to any post-treatment recommendations.
What is the Role of Physical Therapy After Stem Cell Treatment for Osteoarthritis?
"Physical therapy after stem cell treatment for osteoarthritis is crucial for optimizing outcomes by improving joint strength, flexibility, and stability, aiding in functional recovery, and helping integrate the regenerative effects of the stem cells."
Physical therapy plays a vital role in maximizing the benefits of stem cell therapy and supporting long-term joint health. It is often an integral part of the overall treatment plan in Germany.
- Optimizing Joint Mechanics: Physical therapists can guide patients through exercises that improve joint alignment, muscle balance, and movement patterns, which are essential for reducing stress on the treated joint.
- Strengthening and Stability: Targeted exercises help strengthen the muscles surrounding the joint, providing better support and stability, which in turn reduces pain and improves function.
- Increasing Range of Motion: Gentle stretching and mobility exercises help restore and maintain the joint's full range of motion, counteracting stiffness often associated with osteoarthritis.
- Facilitating Healing: Controlled movement and activity can promote blood flow to the treated area, which is beneficial for the healing and regenerative processes initiated by the stem cells.
- Education and Self-Management: Physical therapists educate patients on proper body mechanics, activity modification, and home exercise programs, empowering them to manage their condition long-term and prevent future issues.
A tailored physical therapy program, often starting with gentle exercises and gradually progressing, is typically recommended to complement the stem cell treatment.
What is the Difference Between Stem Cell Therapy and PRP for Osteoarthritis?
"Stem cell therapy uses undifferentiated cells (like MSCs) with the potential to differentiate and promote tissue regeneration, while Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) uses concentrated platelets from the patient's blood to deliver growth factors that stimulate healing and reduce inflammation, both applied for osteoarthritis."
Both stem cell therapy and PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) are regenerative treatments for osteoarthritis, but they differ in their fundamental components and mechanisms:
- Stem Cell Therapy:
- Components: Involves harvesting and concentrating stem cells, primarily mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), from sources like bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue.
- Mechanism: MSCs have the unique ability to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types (like cartilage cells). They also release growth factors and anti-inflammatory molecules, directly influencing tissue repair and reducing inflammation. The focus is on potential regeneration and creating a healing environment.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- Components: Involves drawing a small amount of the patient's blood, which is then centrifuged to separate and concentrate the platelets. Platelets are rich in various growth factors.
- Mechanism: PRP contains a high concentration of growth factors that signal to the body's existing cells to accelerate healing, reduce inflammation, and promote cell proliferation. PRP primarily enhances the body's natural healing response rather than introducing new undifferentiated cells for regeneration.
While both aim to reduce pain and improve function in osteoarthritis, stem cell therapy is generally considered a more advanced and potentially more powerful regenerative treatment due to the unique properties of stem cells themselves, beyond just growth factors. Often, these treatments can be used in combination for enhanced effects.
Explore PlacidWay for solutions related to medical tourism, healthcare services, or other relevant offerings.


.png)




.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)

Share this listing