
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, especially when traditional treatments no longer provide relief. For many UK patients, stem cell therapy in Turkey is emerging as a promising alternative to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Combining advanced medical technology with affordable costs, Turkey has become a leading destination for regenerative treatments like stem cell therapy. In this guide, we’ll explore how the procedure works, its benefits, and what UK patients need to know before traveling for treatment.
Key Takeaways
-
Stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Turkey offers a promising regenerative medicine approach, particularly for UK patients seeking alternative or supplementary treatments when conventional methods fall short.
-
Turkey has emerged as a hub for medical tourism, providing state-of-the-art clinics, experienced specialists, and competitive pricing for stem cell treatments.
-
The primary type of stem cells used for RA therapy are Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), known for their immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Cost for stem cell therapy in Turkey can be substantial compared to Western countries, making it an attractive option for UK patients.
-
Typical cost for Stem Cell Therapy for RA in Turkey ranges from €5,000 to €15,000 (£4,200 to £12,800) per treatment cycle.
-
Comparable treatments in the UK or other Western European countries could range from £10,000 to £30,000+ per cycle, highlighting significant savings.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic, autoimmune condition where your body's immune system targets its own healthy tissues, predominantly in the joints. This leads to persistent pain, swelling, and stiffness, often progressing to joint damage.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a debilitating autoimmune disease that primarily targets the lining of the joints, causing painful swelling that can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity. Unlike the wear-and-tear damage of osteoarthritis, RA affects the lining of your joints (synovium), causing a painful swelling that can lead to joint destruction. It often affects multiple joints simultaneously, typically the small joints in the hands and feet.
Beyond the joints, RA can also impact other body systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent irreversible joint damage and maintain quality of life. The disease course can vary widely among individuals, from mild to severe, with periods of flares and remission.
Traditional Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Conventional treatments for RA focus on managing symptoms, reducing inflammation, slowing disease progression, and preventing joint damage, typically involving medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery.
For many years, the cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis treatment has been a multi-faceted approach aimed at controlling inflammation and preserving joint function. These traditional methods include:
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen can relieve pain and reduce inflammation, but they don't slow disease progression.
-
Corticosteroids: Drugs such as prednisone can quickly reduce inflammation and pain but are generally used for short periods due to potential side effects.
-
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These are the primary long-term treatments for RA. Conventional DMARDs like methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and hydroxychloroquine work by suppressing the immune system to slow the disease.
-
Biologic Agents: A newer class of DMARDs, biologics target specific parts of the immune system that drive inflammation. Examples include etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and rituximab. These are often used when conventional DMARDs are insufficient.
-
Targeted Synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs): Oral small-molecule drugs that target specific pathways inside immune cells, such as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors.
-
Physical and Occupational Therapy: Therapists can teach exercises to keep joints flexible and recommend strategies to perform daily tasks with less joint stress.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged joints, replace joints (e.g., knee or hip replacement), or fuse joints.
While these treatments are effective for many, some patients may not respond adequately, experience severe side effects, or seek complementary therapies. This is where regenerative medicine approaches like stem cell therapy come into consideration.
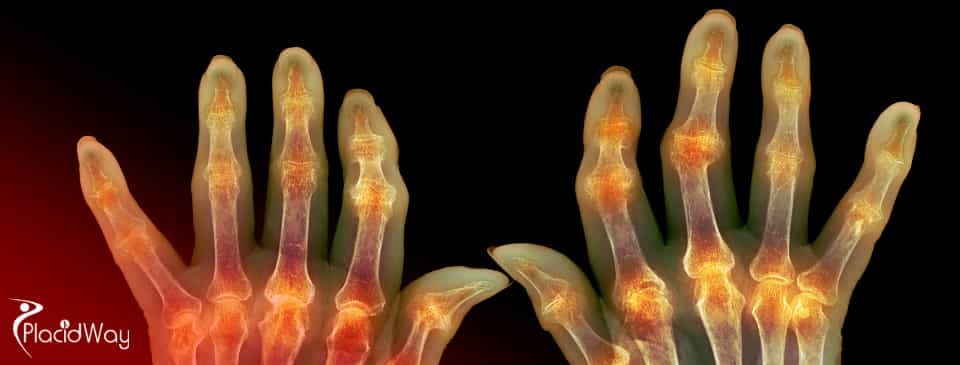
What is Stem Cell Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Stem cell therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis is an innovative regenerative treatment that harnesses the body's own healing capabilities, primarily using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to modulate the immune system, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue repair within affected joints.
Stem cell therapy represents a frontier in treating chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Instead of merely managing symptoms, it aims to address the underlying pathology. For RA, the focus is largely on Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). These are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into various cell types (bone, cartilage, fat) and possess remarkable immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and tissue-regenerating properties.
When introduced into the body, MSCs are believed to:
-
Suppress the overactive immune response: By interacting with immune cells (T cells, B cells, macrophages), MSCs help to rebalance the immune system and reduce the autoimmune attack on joints.
-
Reduce inflammation: They secrete various anti-inflammatory molecules that calm the inflammatory cascade in the synovium.
-
Promote tissue repair: MSCs can potentially contribute to the regeneration of damaged cartilage and other joint tissues, though this is still an area of active research.
-
Secrete trophic factors: These factors support the survival and function of existing cells and promote a healing environment.
Did You Know? The first successful human bone marrow transplant, a form of stem cell therapy, was performed in 1956. Since then, research into different types of stem cells and their therapeutic applications has expanded exponentially.
Types of Stem Cells Used
For Rheumatoid Arthritis, the most commonly used stem cells are Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), primarily derived from adipose (fat) tissue or bone marrow, due to their potent immunomodulatory and regenerative capabilities.
While various types of stem cells exist, Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are the preferred choice for rheumatoid arthritis due to their unique properties. These cells are "adult" stem cells, meaning they are found in various tissues throughout the body, not just embryos.
The primary sources for obtaining MSCs for therapeutic use include:
-
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs): These are harvested from a patient's own fat tissue through a mini-liposuction procedure. ADSCs are abundant, relatively easy to extract, and can be isolated with less discomfort than bone marrow.
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells (BMSCs): These are extracted from the bone marrow, typically from the hip bone (iliac crest), through a procedure called bone marrow aspiration. BMSCs have a long history of therapeutic use.
-
Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (UC-MSCs): These are obtained from donated umbilical cord tissue after a healthy birth. They are considered "allogeneic" (from a donor) but have low immunogenicity, meaning they are less likely to cause an immune reaction. This allows for off-the-shelf availability.
The choice of MSC source often depends on the clinic's expertise, patient preference, and specific treatment protocols. All sources are carefully processed and expanded in a laboratory before administration.
The Stem Cell Therapy Procedure
The stem cell therapy procedure for RA typically involves harvesting the patient's own stem cells (autologous) or using donor cells (allogeneic), processing them, and then administering them back into the patient, often via intravenous infusion or direct joint injection.
The stem cell therapy procedure for rheumatoid arthritis can vary slightly depending on the type of stem cells used (autologous vs. allogeneic) and the clinic's protocol, but generally follows these steps:
-
Consultation and Assessment: An initial comprehensive evaluation, including medical history, current RA status, imaging (X-rays, MRI), and blood tests, to determine candidacy and tailor the treatment plan.
-
Stem Cell Harvesting (for autologous therapy):
-
Adipose Tissue: A minor liposuction procedure is performed, typically under local anesthesia, to extract a small amount of fat from the abdomen or thigh.
-
Bone Marrow: Bone marrow is aspirated from the hip bone using a needle, usually under local anesthesia or sedation.
-
-
Cell Processing and Expansion: The harvested tissue or bone marrow is sent to a specialized laboratory where the MSCs are isolated, purified, and often expanded (multiplied) to achieve the desired therapeutic dose. This process can take several days to a few weeks.
-
Stem Cell Administration:
-
Intravenous (IV) Infusion: The most common method, where the prepared stem cells are infused directly into the bloodstream, allowing them to circulate and potentially home in on inflamed areas.
-
Intra-articular Injection: For localized joint involvement, stem cells may be directly injected into the affected joints.
-
Combination: Some protocols involve both IV infusion and direct joint injections.
-
-
Post-Treatment Monitoring: Patients are monitored for a short period after administration.
The entire process is usually performed on an outpatient basis, though some clinics may recommend a brief observation period. Multiple treatment cycles may be recommended depending on the patient's response and disease severity.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for RA
Stem cell therapy for RA offers potential benefits such as reducing inflammation and pain, improving joint function, modulating the immune system, and potentially slowing disease progression, often providing relief for patients who haven't responded to conventional treatments.
The potential benefits of stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis are particularly appealing for patients seeking alternatives or enhancements to traditional therapies. These include:
-
Significant Reduction in Inflammation: MSCs are known to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines and promote anti-inflammatory ones, leading to a decrease in joint swelling and systemic inflammation.
-
Pain Relief: By reducing inflammation and potentially promoting tissue repair, patients often experience a notable reduction in joint pain.
-
Improved Joint Function and Mobility: Decreased pain and inflammation can lead to greater flexibility, range of motion, and overall improvement in physical function, enhancing daily activities.
-
Immunomodulation: MSCs help to rebalance the dysregulated immune system, moving it away from its self-destructive attack on joint tissues. This is a key advantage over simple immunosuppressants.
-
Potential for Disease Modification: While more research is ongoing, stem cells may have the ability to slow or halt the progression of joint damage, potentially reducing the need for joint replacement surgery in the long run.
-
Reduced Side Effects (Autologous Therapy): When using a patient's own cells (autologous), the risk of immune rejection or adverse reactions is minimal.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life: The cumulative effect of reduced pain, improved function, and decreased disease activity often leads to a significant enhancement in a patient's overall quality of life.
Expert Insight: "Stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis holds immense promise due to its ability to modulate the immune system and promote tissue healing, offering a new paradigm in how we approach this complex autoimmune disease. While it's not a cure, it can provide profound symptomatic relief and potentially alter disease progression for many patients,"
Risks and Side Effects
While generally considered safe, stem cell therapy for RA carries potential risks, including transient fever, mild pain at the injection site, and, rarely, infection or tumor formation, making thorough patient selection and clinic choice crucial.
Although stem cell therapy is often perceived as a natural and safe treatment, it is still a medical procedure with potential risks and side effects that patients should be aware of:
-
Mild and Transient Side Effects: The most common side effects are usually mild and short-lived, including:
-
Fever: Low-grade fever immediately after infusion.
-
Pain or Swelling: At the injection or aspiration site (for autologous cells).
-
Headache or Nausea: Less common, but can occur after IV infusion.
-
-
Infection: As with any invasive procedure (harvesting or injection), there is a small risk of infection. Clinics in Turkey adhere to strict sterilization protocols to minimize this.
-
Immune Reaction (Allogeneic Therapy): While allogeneic MSCs generally have low immunogenicity, there's always a slight theoretical risk of an immune reaction or rejection, though it's rare.
-
Tumor Formation: A major concern often associated with embryonic stem cells, but for adult MSCs used in RA therapy, the risk of tumor formation is considered extremely low, with no conclusive evidence in clinical trials.
-
Contamination: If cells are not processed in a sterile, GMP-certified laboratory, there's a risk of bacterial or viral contamination. This highlights the importance of choosing a reputable clinic.
-
Inefficacy: The therapy may not be effective for all patients, and results can vary.
Choosing a highly reputable clinic in Turkey with stringent safety protocols and experienced medical staff is paramount to minimizing these risks.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery after stem cell therapy for RA is typically minimal, often allowing patients to resume normal activities quickly, but adherence to post-treatment guidelines, including physical activity restrictions and regular monitoring, is important for optimal outcomes.
One of the advantages of stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is that the recovery period is generally much less intensive compared to traditional surgeries.
-
Immediate Post-Treatment:
-
If you received an intravenous (IV) infusion, you might experience mild fatigue, a low-grade fever, or headache for 24-48 hours.
-
If you had intra-articular injections or an autologous stem cell harvest (liposuction or bone marrow aspiration), you might have localized pain, swelling, or bruising at the site for a few days.
-
-
Activity Restrictions: Your doctor will advise on specific restrictions. Generally, strenuous activity or heavy lifting might be discouraged for a few days to a week to allow the body to integrate the cells and minimize stress on the treated areas. Light activity is usually encouraged.
-
Medication Management: Your current RA medications will likely be continued initially. Your Turkish physician will work with your UK rheumatologist (if you have one) to gradually adjust or taper medications based on your response to stem cell therapy. It is crucial not to stop your existing medications without medical advice.
-
Follow-up and Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments, often including blood tests and clinical assessments, are vital to track your progress and evaluate the efficacy of the treatment. Many clinics offer remote follow-up for international patients.
-
Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular light exercise, and avoiding smoking, can support the regenerative process.
Did You Know? Some studies suggest that the beneficial effects of MSCs in autoimmune diseases might not only come from the cells themselves but also from the "paracrine effects" – the release of signaling molecules that influence surrounding cells and tissues.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for RA in Turkey
The cost of stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis in Turkey is significantly lower than in many Western countries, typically ranging from €5,000 to €15,000 per treatment cycle, offering an affordable high-quality option for UK patients.
For UK patients, the cost-effectiveness of stem cell therapy in Turkey is a major draw. The pricing in Turkey is highly competitive while maintaining high standards of medical care. Here's an estimated cost breakdown:
|
Component |
Estimated Cost in Turkey (EUR) |
Estimated Cost in Turkey (GBP) |
Estimated Cost in UK/Western Europe (GBP) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Initial Consultation |
€100 - €300 |
£85 - £250 |
£200 - £500 |
Comprehensive medical review, eligibility assessment. Often included in packages. |
|
Stem Cell Harvesting & Processing |
€2,000 - €5,000 |
£1,700 - £4,200 |
£4,000 - £10,000 |
For autologous (patient's own) cells, includes liposuction or bone marrow aspiration and laboratory processing. Costs vary by source and quantity of cells. |
|
Stem Cell Administration (per cycle) |
€3,000 - €10,000 |
£2,500 - £8,500 |
£6,000 - £20,000+ |
Includes the cost of the cells, administration (IV or injection), and immediate post-treatment monitoring. Allogeneic (donor) cells might be priced differently. Multiple cycles may be recommended. |
|
Total per Treatment Cycle |
€5,000 - €15,000 |
£4,200 - £12,800 |
£10,000 - £30,000+ |
This range covers various clinics and protocols. Most packages will include consultation, harvesting, processing, and administration. |
|
Flights (UK-Turkey return) |
€150 - €500 |
£130 - £430 |
N/A |
Varies by airline, booking time, and airport. |
|
Accommodation (1 week) |
€300 - €800 |
£250 - £680 |
N/A |
Depending on hotel class and location. |
|
Translation Services |
€50 - €150 per day |
£40 - £120 per day |
N/A |
Often included in medical tourism packages or provided by clinics. |
|
Post-treatment Medications |
€50 - €200 |
£40 - £170 |
£50 - £200+ |
Any specific medications needed after the stem cell treatment. |
Note: The exchange rate used for conversion (GBP to EUR) is approximate and subject to fluctuations. Always obtain a personalized, all-inclusive quote from your chosen clinic or medical tourism facilitator.
Why Choose Turkey for Stem Cell Therapy for RA?
Turkey is a prime destination for stem cell therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis due to its high-quality medical infrastructure, internationally accredited clinics, experienced specialists, and competitive pricing, making advanced treatments accessible to UK patients.
For UK patients considering stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis, Turkey presents a highly attractive option with several key advantages:
-
Advanced Medical Facilities: Turkey boasts modern hospitals and clinics equipped with state-of-the-art technology, including specialized laboratories for stem cell processing and administration. Many facilities are internationally accredited (e.g., JCI – Joint Commission International).
-
Experienced Specialists: Turkish doctors and medical teams, particularly in fields like rheumatology and regenerative medicine, are highly qualified, often trained in Western countries, and have extensive experience in administering stem cell treatments.
-
Competitive Pricing: As highlighted in the cost table, the cost of stem cell therapy in Turkey is significantly more affordable compared to the UK, USA, or Western Europe, without compromising on quality of care. This makes innovative treatments accessible to a wider range of patients.
-
High-Quality Patient Care: Turkish clinics are known for their patient-centric approach, offering personalized care, comfort, and often luxurious facilities that enhance the overall patient experience.
-
Accessibility and Travel Ease: Turkey is easily accessible from the UK with numerous direct flights to major cities like Istanbul and Ankara, which are home to many leading medical facilities. Visa requirements for UK citizens are generally straightforward.
-
Cultural Experience: Patients can combine their treatment with a unique cultural experience, enjoying Turkey's rich history, beautiful landscapes, and renowned hospitality.
.png)
Preparing for Your Medical Journey to Turkey
Thorough preparation for your medical journey to Turkey involves comprehensive medical documentation, travel logistics, and understanding the clinic's support services to ensure a smooth and stress-free experience.
Planning for stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis in Turkey requires careful organization:
-
Initial Contact and Consultation: Begin by reaching out to a reputable medical tourism facilitator like PlacidWay or directly to a Turkish clinic specializing in stem cell therapy for RA. Provide your complete medical history, including RA diagnosis, disease activity, current medications, and any previous treatments. This will facilitate an initial remote consultation with a Turkish specialist.
-
Medical Records: Compile all relevant medical records from your UK rheumatologist and general practitioner. Ensure they are organized and, if necessary, translated into English (which is widely understood in Turkish medical tourism settings) or Turkish. Key documents include diagnosis reports, blood tests (e.g., CRP, ESR, ANA, RF, anti-CCP), imaging reports (X-rays, MRI of affected joints), and a list of all current medications and dosages.
-
Travel and Accommodation:
-
Passport: Ensure your UK passport is valid for at least six months beyond your intended departure date from Turkey.
-
Visa: UK citizens generally do not require a visa for short tourist or medical stays in Turkey (up to 90 days within a 180-day period). Always check the latest requirements before travel.
-
Flights: Book your flights well in advance for better rates and availability. Major airports like Istanbul Airport (IST) and Sabiha Gökçen International Airport (SAW) are well-connected to the UK.
-
Accommodation: Your medical tourism facilitator or clinic can assist with booking accommodation, often at partner hotels close to the facility.
-
Travel Insurance: Secure comprehensive travel and medical insurance that specifically covers overseas medical treatment and any potential complications. This is crucial for peace of mind.
-
-
Financial Planning: Clarify all costs with the clinic or facilitator, including the treatment, accommodation, transfers, and any additional services. Understand payment schedules and accepted payment methods. Be aware of currency exchange rates (Turkish Lira to GBP) and international transaction fees.
-
Communication: While many medical staff in Turkey speak English, confirm if translation services will be provided, especially for detailed medical discussions.
-
Pre-Treatment Instructions: Adhere strictly to any pre-treatment instructions from your Turkish medical team, which might include specific dietary guidelines, temporary cessation of certain medications, or other preparations.
Life After Stem Cell Therapy for RA
Life after stem cell therapy for RA can bring significant improvements in symptoms, joint function, and overall quality of life, often leading to reduced reliance on conventional medications and a more active lifestyle, though continued monitoring and adherence to a healthy lifestyle are essential.
The aim of stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is to provide lasting relief and improve the patient's condition. What you can expect in the months following treatment:
-
Gradual Improvement: The effects of stem cell therapy are often not immediate. Many patients report a gradual improvement in symptoms, such as decreased pain, reduced morning stiffness, and improved joint mobility, over several weeks to months as the cells work to modulate the immune system and promote healing.
-
Reduced Medication Dependence: For some patients, successful stem cell therapy may lead to a reduction in the dosage or frequency of their traditional RA medications (DMARDs, biologics), or even, in some cases, temporary discontinuation, always under strict medical supervision.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life: With improved symptoms and joint function, patients often experience a significant enhancement in their ability to perform daily activities, engage in hobbies, and enjoy a more active and fulfilling life.
-
Long-term Monitoring: Continued communication with your Turkish medical team and your UK rheumatologist is vital. Regular follow-up appointments, even if remote, will help monitor your long-term progress and ensure any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan are made.
-
Maintenance of a Healthy Lifestyle: To support the long-term benefits of stem cell therapy, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced anti-inflammatory diet, regular gentle exercise (as approved by your doctor), adequate sleep, and stress management, is highly recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is stem cell therapy for RA a cure?
No, stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is not currently considered a cure but rather a promising regenerative medicine treatment aimed at modulating the immune system, reducing inflammation, and improving symptoms, potentially leading to long-term remission or significant disease control.
How long do the effects of stem cell therapy for RA last?
The duration of the effects of stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis varies among individuals, but many patients report sustained benefits lasting from several months to a few years, with some opting for repeat treatments to maintain results. Factors influencing the longevity of the effects include the severity of the disease, the patient's overall health, and the specific protocol used. Your doctor in Turkey will discuss expected outcomes based on your individual case.
Are the stem cells used from donors or my own body?
For rheumatoid arthritis, clinics in Turkey typically use either autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), harvested from your own fat or bone marrow, or allogeneic MSCs derived from donated umbilical cords, both of which are considered safe and effective.
How many stem cell treatments will I need for RA?
The number of stem cell treatment cycles needed for rheumatoid arthritis varies based on individual response and disease severity; some patients may achieve significant relief with one cycle, while others might benefit from multiple cycles over time. Your Turkish specialist will assess your progress after each treatment cycle and recommend further steps based on your clinical improvement and disease markers.
Is stem cell therapy for RA approved in the UK?
Currently, stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is generally not a standard, approved treatment within the NHS in the UK outside of clinical trials, which is why many UK patients explore options in countries like Turkey where it is more widely available through private clinics.
What should I consider when choosing a clinic in Turkey for stem cell therapy?
When choosing a stem cell clinic in Turkey, prioritize those with international accreditations (e.g., JCI), experienced specialists in rheumatology and regenerative medicine, transparent pricing, a clear treatment protocol, and comprehensive patient support, including follow-up care and language services. It's also important to check patient testimonials and ensure the clinic operates a GMP-certified laboratory for cell processing to ensure safety and quality.
Will stem cell therapy interfere with my current RA medications?
Your Turkish medical team will carefully review your current rheumatoid arthritis medications and provide specific guidance; typically, you will continue your medications initially, and any adjustments will be made gradually under medical supervision based on your response to stem cell therapy.
Restore Your Wellness with PlacidWay
Are you a UK patient suffering from rheumatoid arthritis and exploring advanced treatment options? PlacidWay is your dedicated partner in connecting you with leading stem cell therapy clinics in Turkey.






.png)
.jpg)








Share this listing